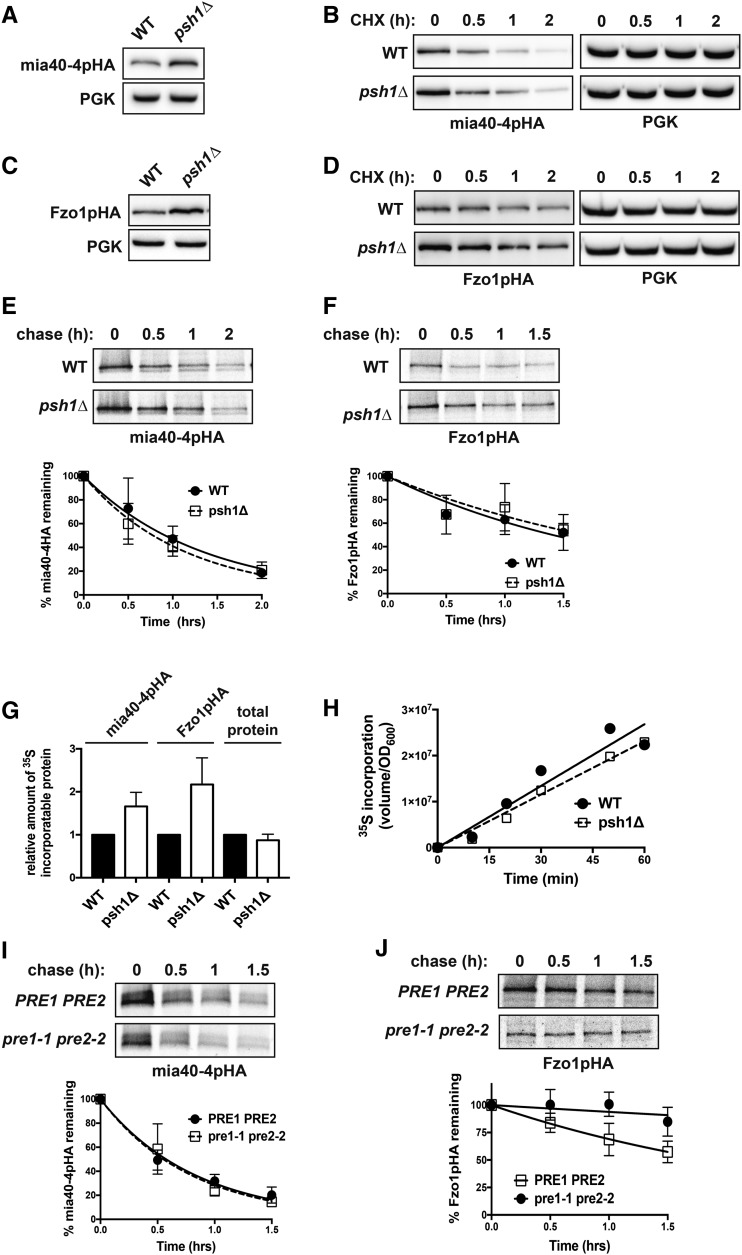
Figure 2.
Loss of Psh1p affects the steady-state levels of mia40-4pHA and Fzo1pHA, without affecting their rates of turnover or total cellular protein levels. (A) The steady-state protein level of CEN plasmid-expressed mia40-4pHA was assessed at 37° in WT and psh1Δ cells by immunoblotting with HA antibody. PGK serves as a control for equal loading. (B) CHX chase for the indicated times assessing turnover of mia40-4pHA expressed from a CEN plasmid in WT and psh1Δ yeast cells. Proteins were detecting by immunoblotting. (C) The steady-state protein levels of Fzo1pHA, analyzed as in (A) except at 30°. (D) CHX chase of Fzo1pHA, analyzed as in (B) except at 30°. (E) Representative 35S pulse-chase analysis to assess turnover of mia40-4pHA in WT and psh1Δ cells at 37° at the indicated time points. The mean of three independent experiments is graphed below, with error bars depicting the SD. (F) Representative 35S pulse-chase analysis of the turnover of Fzo1pHA in WT and psh1Δ at 30° at the indicated time points, analyzed and graphed as in (E). (G) Quantification of 35S incorporated into mia40-4pHA, Fzo1pHA, or total protein during a 30-min pulse with 35S-labeled methionine/cysteine in psh1Δ and WT strains. Values were normalized to the incorporation in the WT strain. The average and SD of three independent experiments is shown. (H) The rate of total protein synthesis in WT and psh1Δ strains was measured by analyzing 35S methionine/cysteine incorporation into total protein relative to cell density (OD600) over time. (I) Representative 35S pulse-chase analysis of the turnover of mia40-4pHA in a pre1-1 pre2-2 proteasome mutant strain and its PRE1 PRE2 isogenic WT strain, analyzed and graphed as in (E). (J) Representative 35S pulse-chase analysis of the turnover of Fzo1pHA in a pre1-1 pre2-2 proteasome mutant strain and its PRE1 PRE2 isogenic WT strain, analyzed and graphed as in (F).