Figure 1.
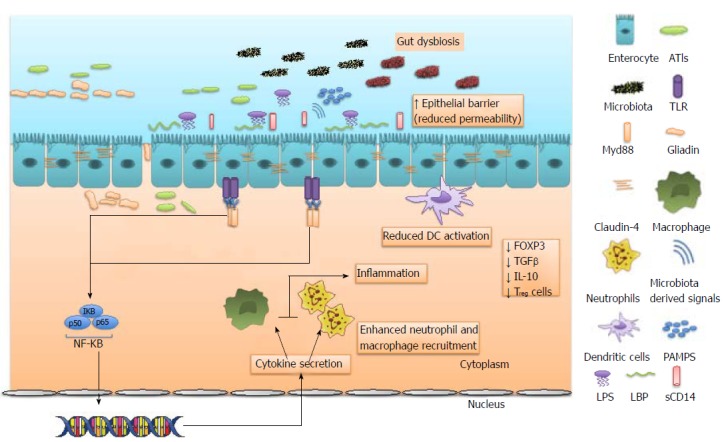
Toll like receptors act as primary sensors to gliadin and non-gluten proteins like alpha amylase/trypsin inhibitors, and microbiota derived signals in non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Dysregulated microbiota also release lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in circulation which result in production of LPS-binding protein (LBP) from gastrointestinal and hepatic epithelial cells and soluble CD14 (sCD14) from monocytes/macrophages. This leads to activation of transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB), which controls the expression of an array of inflammatory cytokine genes resulting in recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages. In contrast to CD, there is limited dendritic cell activation, resulting in reduced expression of Treg cells, reduced FOXP3, TGFβ, IL-10. All these factors with increased expression of claudin-4 culminate in reduced intestinal permeability and increased epithelial barrier. Gut dysbiosis can also promote inflammation through expansion of pro-inflammatory pathobionts. TLRs: Toll like receptors.
