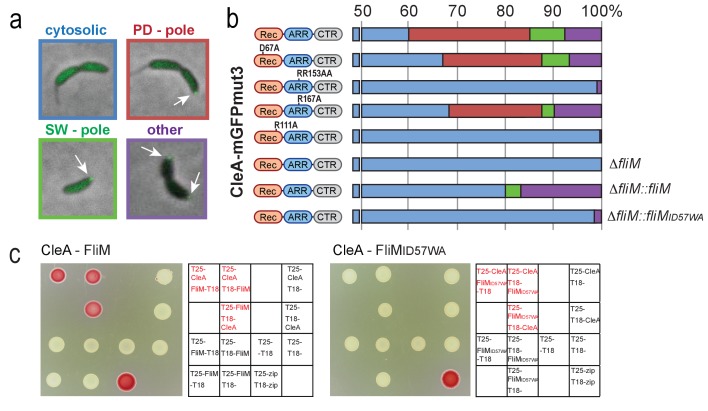
Figure 4. CleA localizes to the flagellated cell pole to interact with FliM.
Examples of the subcellular localization of CleA-mGFPmut3 are shown in (a) and quantified as shown in (b). Variants of CleA fused to mGFPmut3 are indicated on the left with the three domains highlighted as in Figures 2 and 3. Individual amino acid substitutions are indicated. CleA fusion proteins were expressed in a ΔcleA deletion strain and additional genetic alterations as indicated on the right of each panel. Cells were classified according to the localization patterns shown in (a): delocalized cytosolic (blue); foci at flagellated pole of PD cells (red); polar foci in small SW cells (green); other localization patterns (purple), including PD cells with foci at both poles, PD cells with foci at stalked pole, cells with no GFP signal. Number of cells analyzed (top to bottom): 3452, 1450, 637, 2357, 2603, 795, 1148, 1347. (c) CleA interacts with the FliM flagellar switch protein. Binding of CleA to the N-terminus of FliM was determined by bacterial two-hybrid analysis. Fusion proteins between the T25 and T18 fragments of adenylate cyclase (Karimova et al., 1998) and the N-terminal peptide of FliM or FliM_ID57WA (aa 2–65), or full-length CleA were constructed and expressed in the E. coli cya mutant strain AB1770. Strains harboring combinations of FliM and CleA fusions were spotted on McConkey agar plates to score for interaction. Red color indicates reporter gene expression from a cAMP-dependent promoter. The spotting order is indicated in the grids on the right. A positive control with the adenylate cyclase fragments fused to the leucine zipper region of the yeast GCN4 protein (zip) is shown (lower right spots).