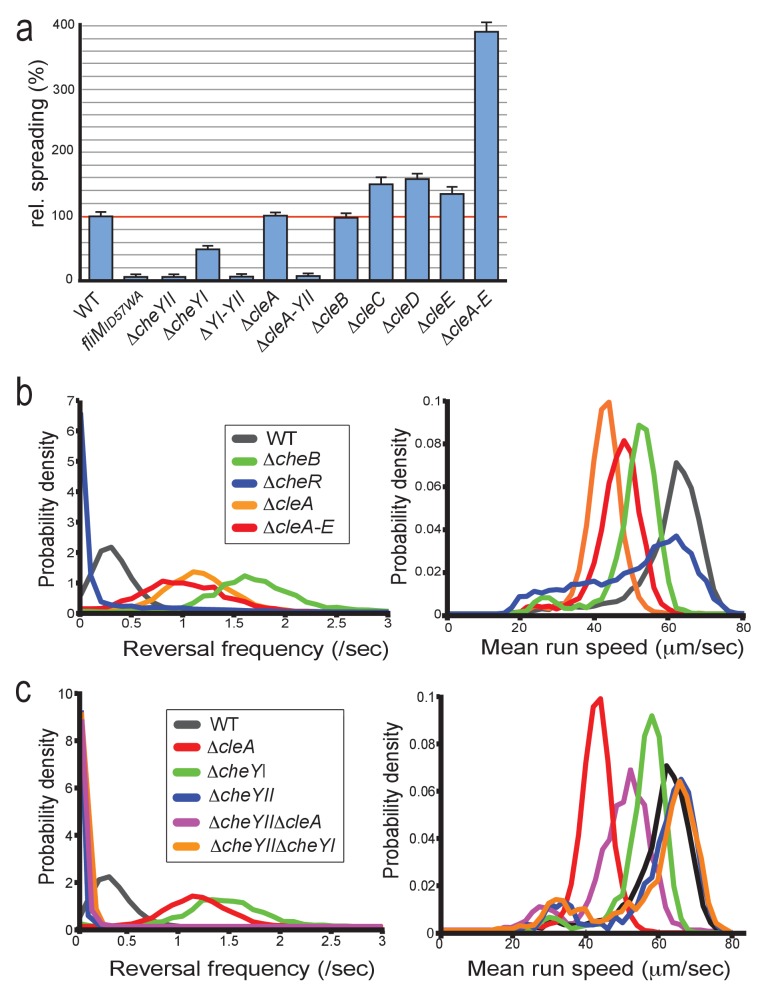
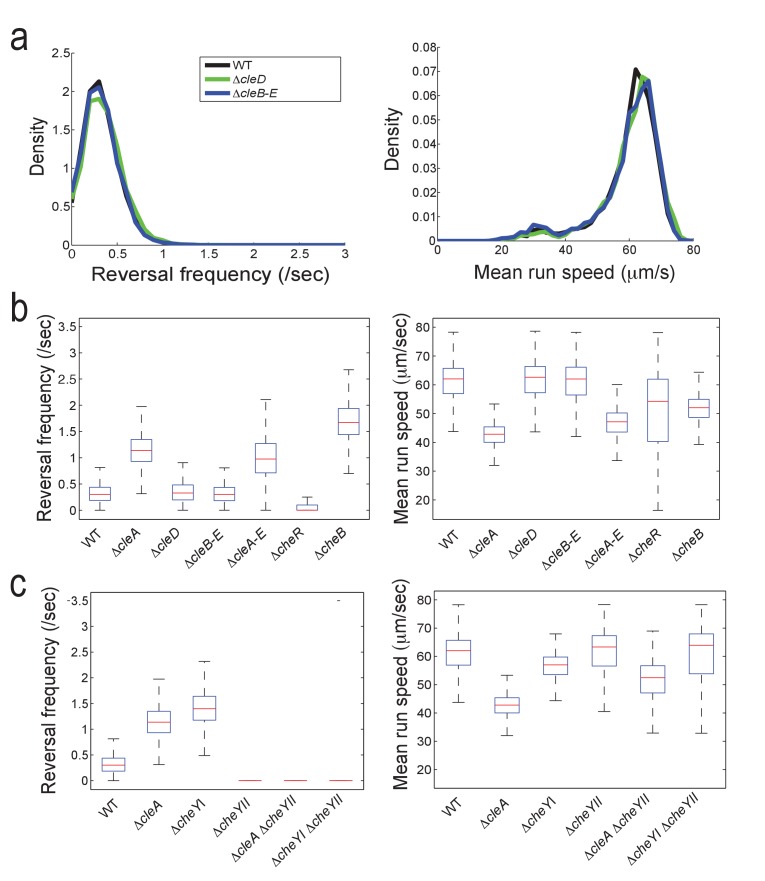
Figure 5. CleA tunes the flagellar motor by interfering with the chemotaxis response.
(a) Cle proteins impede spreading on semisolid agar. Relative spreading areas of C. crescentus wild type and fliM, cheY and cle mutants are indicated. Strains were incubated at 30°C and motility was scored after 72 hr as the overall area covered by individual strains. Strains containing single or multiple deletions are indicated. (b) Mutants lacking CleA show a hyper-reversal phenotype. Directional reversal frequencies and mean run speed were measured for individual swimming cells of C. crescentus wild type and mutants lacking CheB, CheR, CleA, or all five Cle proteins. All strains analyzed harbored an additional deletion in the pilA gene to avoid pili-mediated motility variations. Cells were located in a pseudo-2D environment and their swimming trajectories were recorded at 16 frames per second. The fraction of cells with a given reversal frequency (left) or mean run speed (right) is indicated. (c) CleA promotes smooth swimming by antagonizing the major C. crescentus CheY, CheYII. Analysis of reversal frequencies and mean speed of the strains indicated was as in (b). It should be noted that the reversal frequency profiles of strains ΔcheYII, DcheYIIΔcleA and ΔcheYIIΔcheYI overlay. Experiments in (b) and (c) include the analysis of >850 cells for each strain.