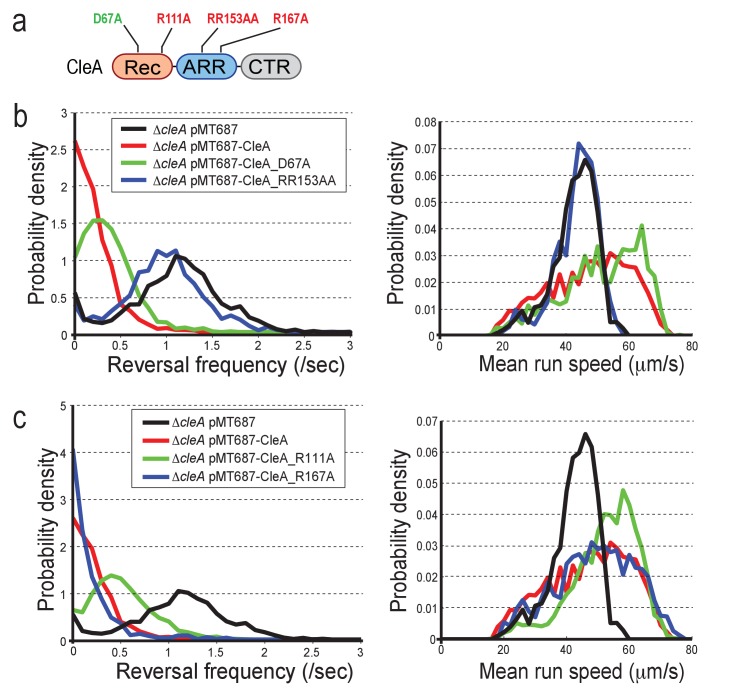
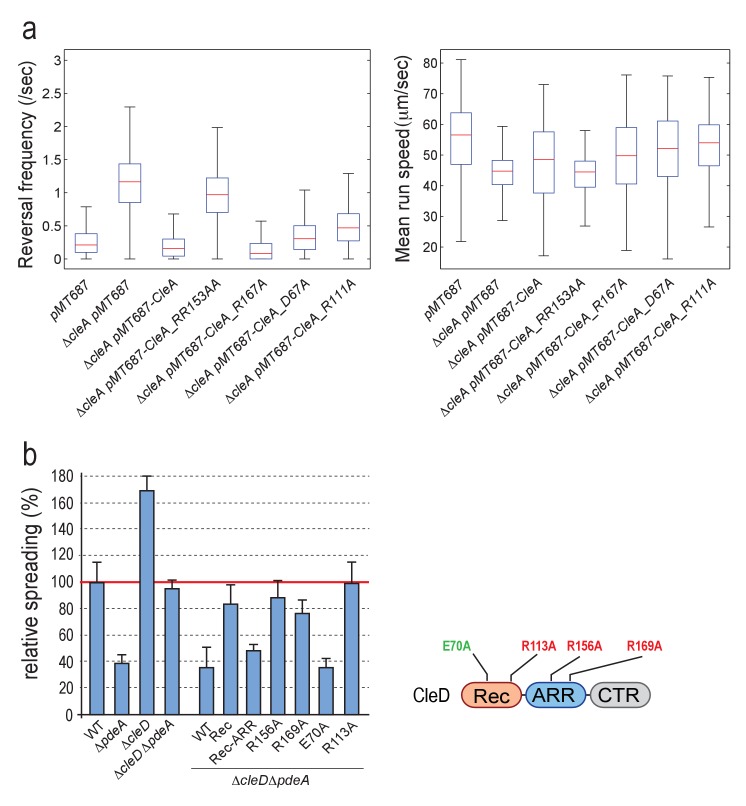
Figure 7. CleA is activated by c-di-GMP binding but not phosphorylation.
(a) Schematic of the domain structure of CleA with mutations that interfere with potential phosphorylation control (green) or c-di-GMP binding (red). The domains are labeled as in Figures 2, 3 and 4. (b-c) CleA is activated by c-di-GMP binding. Single cell analysis of reversal frequencies and mean speed of C. crescentus wild type andΔcleA mutants harboring plasmid driven cleA alleles as indicated in (a). cleA alleles were expressed from a xylose-dependent promoter and were induced with 0.1% xylose for 3 hr before imaging. Experiments in (b) and (c) include the analysis of >850 cells for each strain.