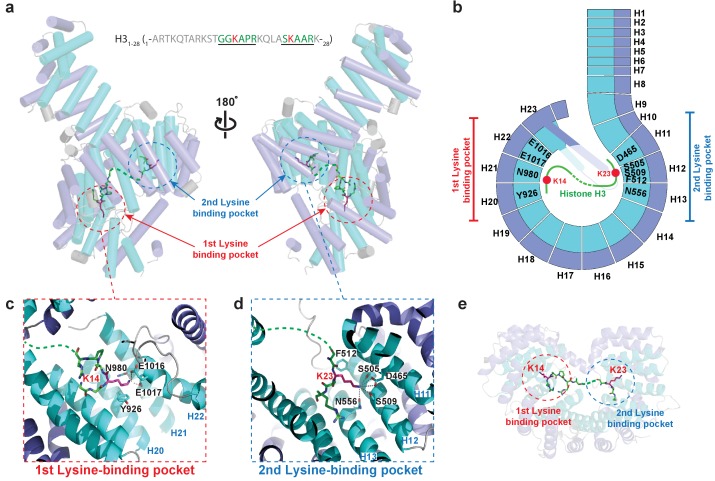
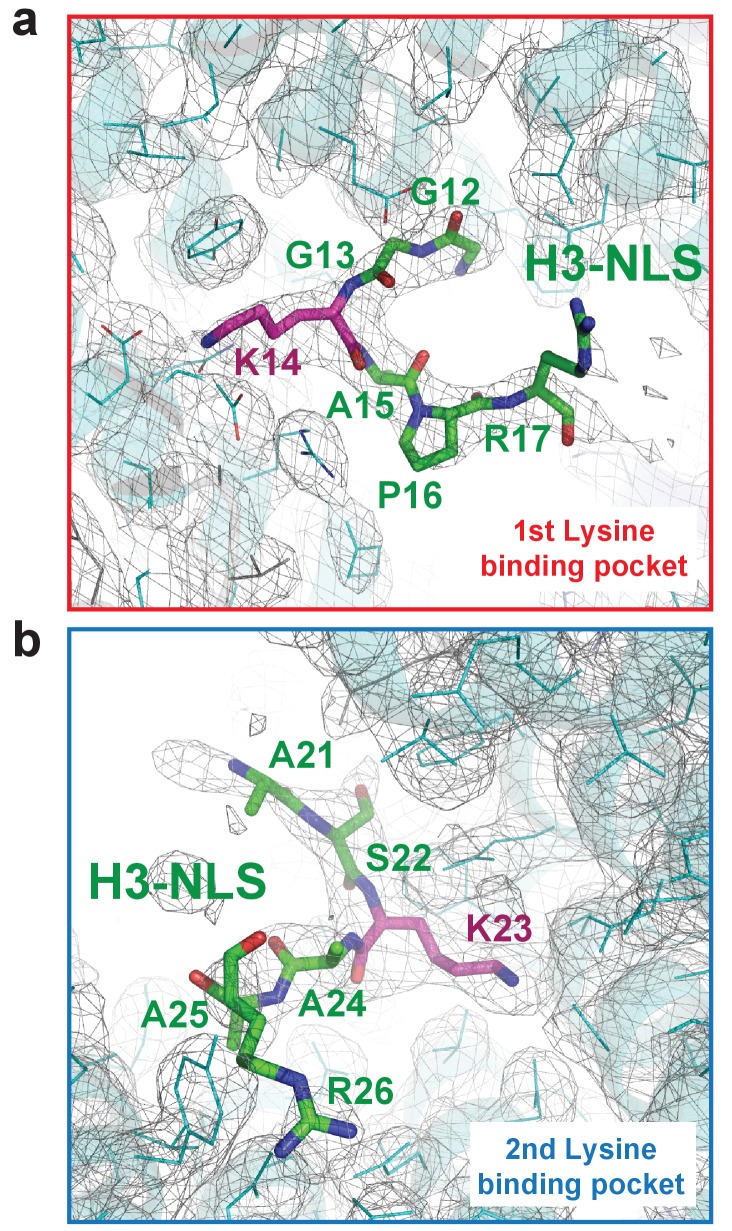
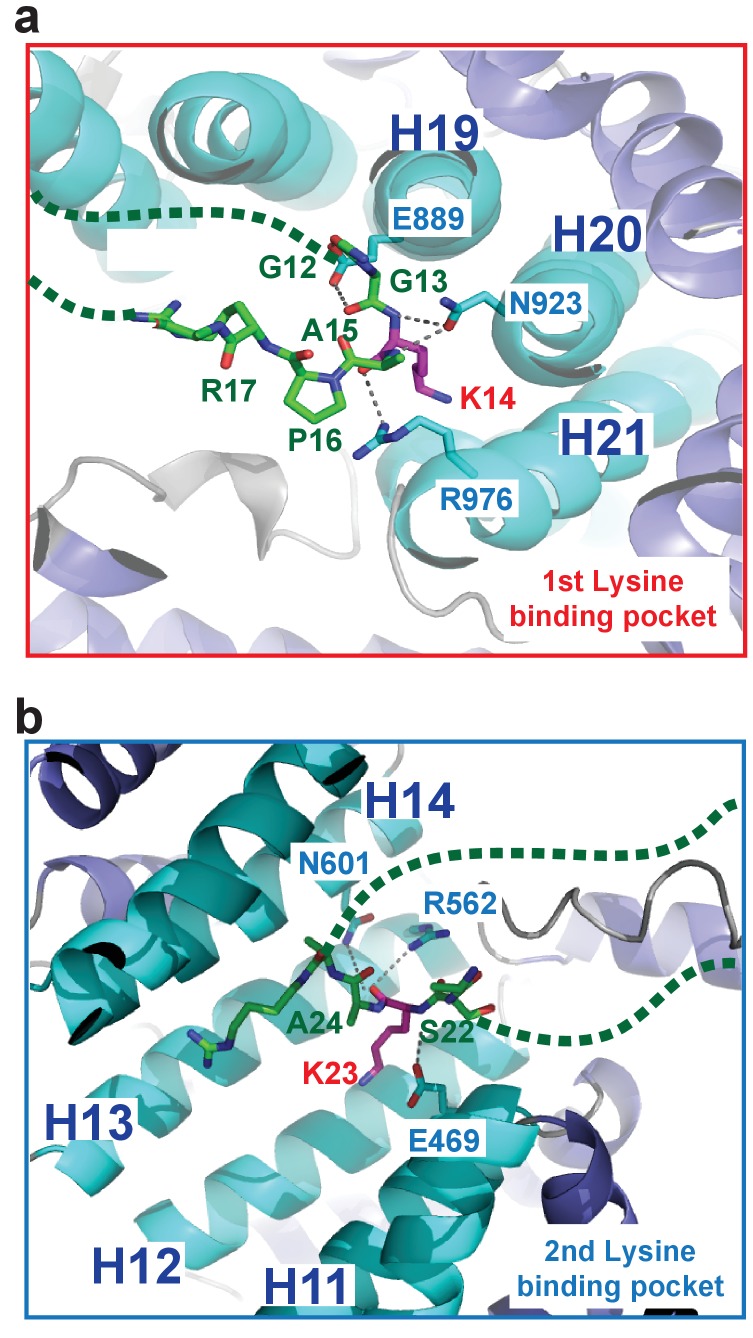
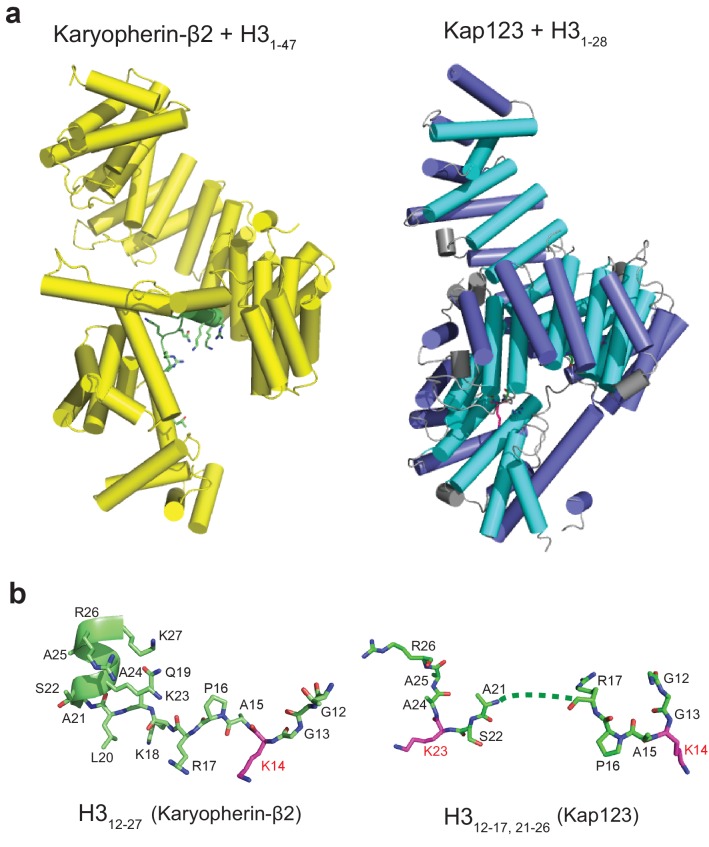
Figure 2. Crystal structure of Kl Kap123 in complex with H31–28-NLS.
(a) Crystal structure of full-length Kl Kap123 in the presence of H31–28-NLS (green stick model, 1-ARTKQTARKSTGGKAPRKQLASKAARK-28) with two lateral views (180° rotation). The two lysine-binding pockets located at the inner curvature of Kap123 are marked with red (first lysine-binding pocket) and blue (second lysine-binding pocket) dashed circles. Residues 12–17 and 21–26 of H31–28-NLS (chain B) are ordered and visible in the structure. The two lysine residues (H3 K14 and K23) that bind to these lysine-binding pockets of Kap123 are colored red. (b) Schematic view of Kl Kap123 in complex with H31–28-NLS. The residues and HEAT repeats that participate in organizing two lysine-binding pockets are described. (c) The first lysine-binding pocket of Kl Kap123. K14 of H31–28-NLS forms hydrophobic (Y926) and electrostatic/hydrogen bond (N980, E1016, and E1017) interactions with Kap123 through repeats 20–22. (d) The second lysine-binding pocket of Kl Kap123. K23 of H31–28-NLS makes hydrophobic (Y512) and electrostatic/hydrogen bond (D465, S505, S509, and N556) interactions with Kap123 through repeats 11–13. (e) Top view of Kl Kap123 in complex with H31–28-NLS. Two lysine-binding sites are distally located and the middle region of H31–28-NLS does not make any specific contacts with Kap123.