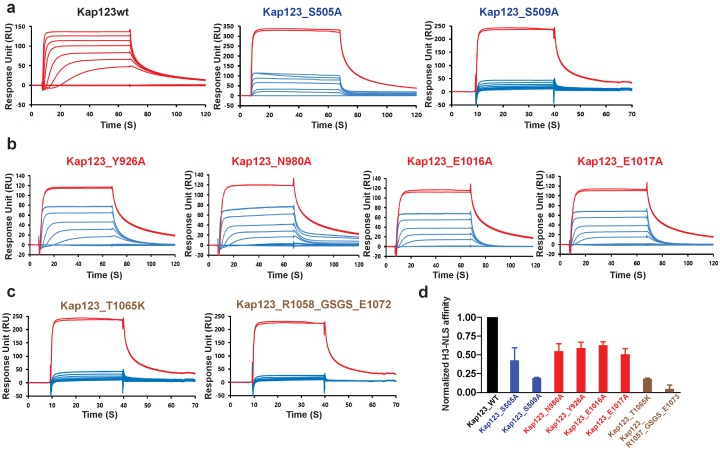
Figure 3. Surface plasmon resonance analysis of wild-type and mutants Kl Kap123 in the presence of H31–35-NLS.
The biacore diagrams of Kl Kap123 wild-type and mutants in the presence of H31–35-NLS peptides are listed. (a) Streptavidin was immobilized at 400 resonance units (RU) and the C-terminal biotinylated histone H3 peptide (residues 1–35) was captured at 150 RU on a CM5 chip. The wild-type Kap123 was injected with different concentrations (0, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 250, and 500 nM) and sensorgrams are colored red. To monitor the affinity of Kap123 mutants at the second lysine-binding pocket (S505A and S509A), the C-terminal biotinylated histone H3 peptide was captured (300 RU) on a streptavidin-immobilized CM5 chip (400 RU). Various concentrations of Kap123_S505A (0, 65, 125, 250, 500, 1000, and 2000 nM) and Kap123_S509A (0, 32, 65, 125, 250, 500, 1000, and 2000 nM) were injected; their sensorgrams are shown in blue. (b) Affinity measurement of first lysine-binding pocket mutants of Kap123 (Y926A, N980A, E1016A, and E1017A). Streptavidin (400 RU) and C-terminal biotinylated histone H3 peptide (150 RU) were immobilized on a CM5 chip. The mutant proteins were injected with various concentrations (0, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 250, and 500 nM) and sensorgrams are shown in blue. (c) Affinity measurement of Kap123 mutants in the extended helix of the repeat 23. Either the point mutation (T1065K) or the deletion mutant (1058-GSGS-1072; residues 1059–1071 are replaced by the GSGS linker) of Kap123 was injected with various concentrations (0, 32, 65, 125, 250, 500, 1000, and 2000 nM for T1065K and 0, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 250, and 500 nM for 1058-GSGS-1072). Red-colored sensorgrams are positive controls of wild-type Kap123, which we injected at 2000 nM wild-type Kap123 before and after sample injection (a–c). (d) Normalized affinity of wild-type and mutant Kap123s toward H3-NLS is shown in the bar graph. The relative affinity of wild-type and mutant Kap123s measured at five different concentrations is used to generate error bars.