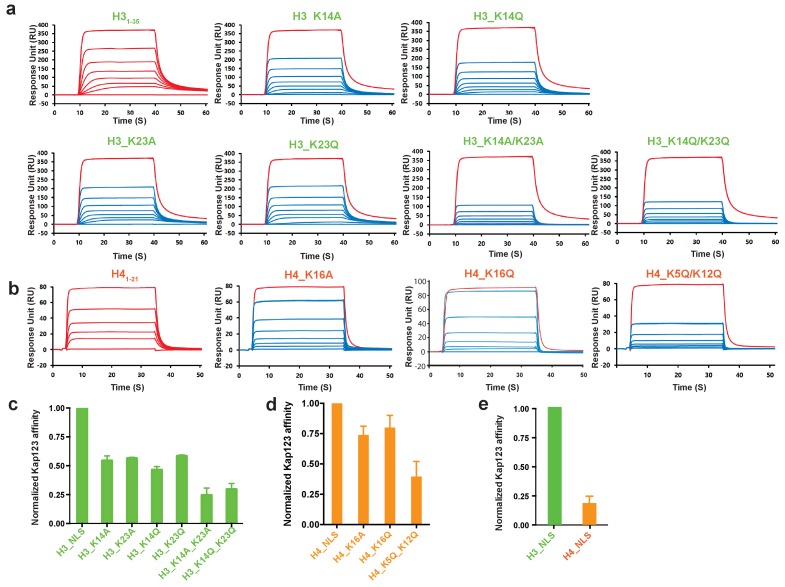
Figure 5. Surface plasmon resonance analysis of wild-type Kl Kap123 in the presence of wild-type or mutants of H31–35-/H41–21-NLSs.
The biacore diagrams (a) and the normalized bar graph (c) of wild-type Kap123 in the presence of wild-type or mutant H31-35-NLS. The wild-type Kap123 was immobilized on a CM5 chip with 7500 RU and the wild-type or mutant H31–35-NLS peptides (H3_K14A, H3_K14Q, H3_K23A, H3_K23Q, or H3_K14Q/K23Q) were injected at different concentrations (0, 0.07, 0.15, 0.32, 0.65, 1.25, 2.5, and 5 μM). The biacore diagrams (b) and the bar graph (d) of wild-type Kap123 in the presence of wild-type or mutant H41–21-NLS. The wild-type Kap123 was immobilized on a CM5 chip with 7116 RU and the wild-type or mutant H41–21-NLS peptides (H4_K16A or H4_K5Q/K12Q) were injected at different concentrations (0, 0.32, 0.62, 1.25, 2.5, 5, and 10 μM). The H4K16Q peptide was used at different concentrations (0, 0.7, 1.5, 3, 6, 12, and 25 uM). See details in Materials and method section. Red-colored sensorgrams represent positive controls of wild-type Kap123, which were injected 2000 nM wild-type Kap123 before and after sample injection (a–b). The relative binding between wild-type Kap123 and mutant peptides was measured at five different concentrations for generating error bars (c–e). (e) The normalized affinity bar graph of H3-/H4-NLS toward wild-type Kap123 was derived from (a) and (b).