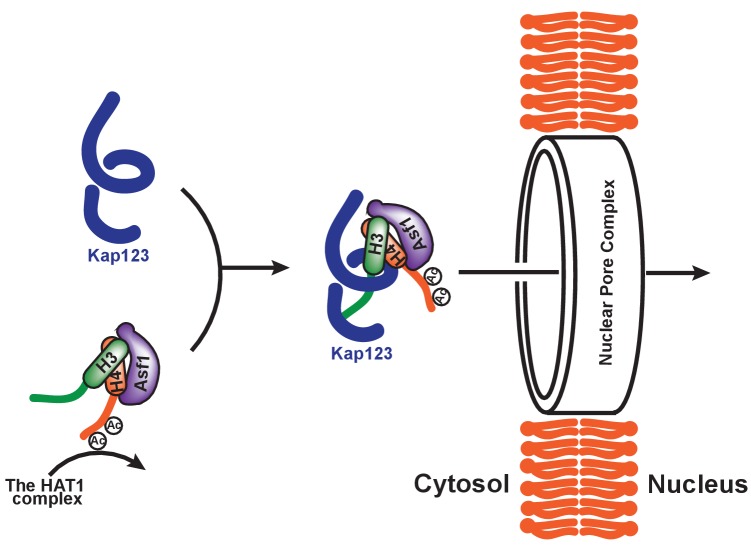
Figure 7. Proposed model of Kap123-dependent nuclear translocation of the H3:H4/Asf1 complex.
Schematic model of the potential role of histone H4 diacetylation during nuclear import. Newly synthesized histones H3 and H4 are associated and immediately protected by its specific chaperone, Asf1. The HAT1 complex subsequently acetylates K5 and K12 of histone H4 as a part of the H3:H4/Asf1 complex. Diacetylation of the H4-NLS, whose affinity toward Kap123 is already fivefold weaker than H3-NLS, further destabilizes the Kap123-histone H4 interaction. Therefore, Kap123 preferentially associates with the H3-NLS and allows for histone H3-dependent Kap123 association during nuclear translocation. It should be noted that there are several histone H3 variants available in eukaryotes but there is only one known histone H4 protein, which can be commonly shared by each histone H3 variant.