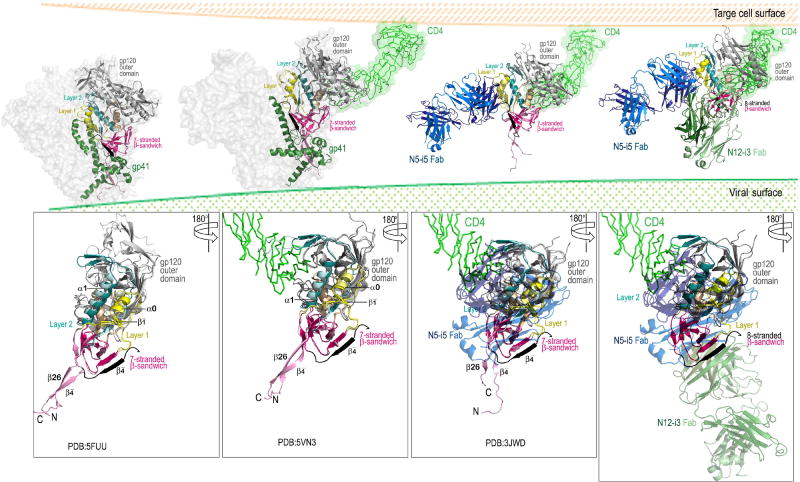
Figure 6. Model of the exposure of the Cluster A epitopes during the entry process.
In the pre-fusion Env trimer both epitopes are occluded by the interaction between gp120 and gp41 with the gp120 N and C termini clasped by gp41 (left panel). Binding of CD4 to the outer domain of gp120 induces formation of the co-receptor binding site which includes conformational changes to the gp120 inner domain (panel two from left). These changes to mobile layers 1 and 2 of the inner domain create the N5-i5 epitope and disrupt the gp120-gp41 interaction (panel three from left). Binding of co-receptor or further opening up of the trimer disengage the N-terminus of gp120 from the gp41 clasp. The N-terminus is then free to form the eighth strand of the inner domain β-sandwich creating the N12-i3 epitope (rightmost panel). Figures were assembled using available structures of the Env pre-fusion trimer (Cry-EM structure of cleaved wild type JR-FL Env trimer in complex with PGT151 Fab, PDB: 5FUU), CD4-triggered Env trimer (Cryo-EM structure of a B41 SOSIP Env trimers in complex with CD4 and antibody 17b, PDB: 5VN3) and 48d Fab-N/C-termini-gp120Hxbc2coree–CD4 complex (PDB: 3JWD) on which N12-i3 Fab/N5-i5 Fab- N/C-termini-gp12093TH057 -coree-M48U1 complex was superimposed. The bottom panels show the gp120 subunit only.