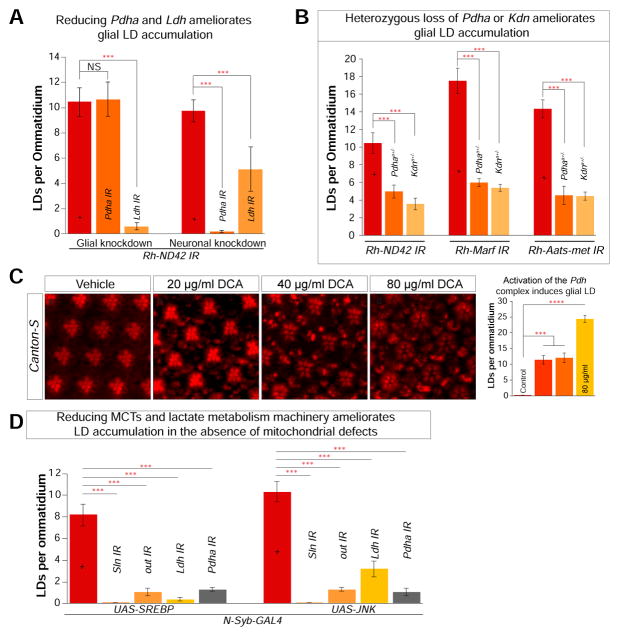
Figure 4. Neuronal lactate is critical for glial LD accumulation.
A) Quantification of LD. Glial (54C-GAL4) or neuronal (Elav-GAL4) specific knockdown of Ldh and Pdha results in a decrease of LD accumulation in the Rh-ND42 IR background. B) Removal of a copy of PdhaA and KdnA reduces glial LD accumulation in the Rh-ND42 IR, Rh-Marf IR and Rh-Aats-met IR flies. C) Flies fed with dichloroacetate (DCA) exhibit a dose dependent increase in glial LD. D) Neuronal overexpression (N-Syb-GAL4) of SREBP or JNK leads to glial LD accumulation. Knockdown of MCTs (Sln, out) and metabolic enzymes (Ldh and Pdha) in the N-Syb-GAL4 overexpression background ameliorates glial LD accumulation. All data points represent mean +/− SEM (Student’s t-test. n > 10 animals each *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0005).