Figure 5. hGle1B interaction with hNup42 is required for mRNA export.
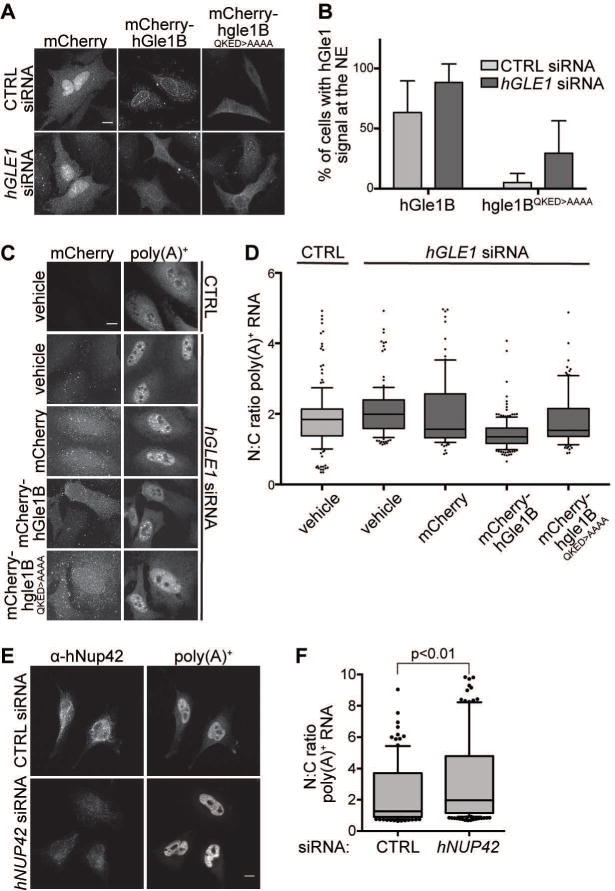
(A–B) mCherry-hgle1BQKED>AAAA is localized to the nuclear rim in a portion of cells. (A) HeLa cells expressing exogenous siRNA-resistant mCherry-hGLE1BR and mCherry-hgle1BR-QKED>AAAA after treatment with CTRL or hGLE1 siRNA were imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bar=10μm. (B) Quantification of cells with rim-localized mCherry signal from the experiment in A. Approximately sixty cells were quantified from three independent experiments, and the mean is indicated with standard error indicated by error bars. (C-D) mCherry-hgle1BQKED>AAAA does not rescue the mRNA export defect upon hGLE1 knockdown. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with mCherry, mCherry-hGLE1BR or mCherry-hgle1BR-QKED>AAAA plasmids following CTRL or hGLE1 knockdown. After fixation, cells were processed for in situ hybridization using 488-labeled oligo d(T) probe followed by mCherry immunofluoresence. Scale bar=10μm. (D) Quantification of nuclear:cytoplasmic mean fluorescence intensity of oligo d(T) signal. Approximately 100 cells were quantified per condition from three independent experiments with nuclear:cytoplasmic intensity ratio depicted in box and whisker plots (whiskers representing 10%–90%). Statistical analysis includes ANOVA with a post-hoc t-test. (E-F) hNUP42 depletion results in a poly(A)+ mRNA export defect. (E) HeLa cells were transfected with CTRL or hNUP42 siRNA for 72h. After fixation, cells were processed for in situ hybridization using Cy3-labeled oligo d(T) probe followed by hNup42 immunofluorescence. Scale bar=10μm. (F) Quantification of nuclear:cytoplasmic mean fluorescence intensity of oligo d(T) signal. Approximately 200 cells were quantified per condition from three independent experiments with nuclear:cytoplasmic intensity ratio depicted in box and whisker plots (whiskers representing 10%–90%). A t-test was performed to analyze statistical significance.
