Figure 7. Schematic for Nup42 function at the NPC cytoplasmic face.
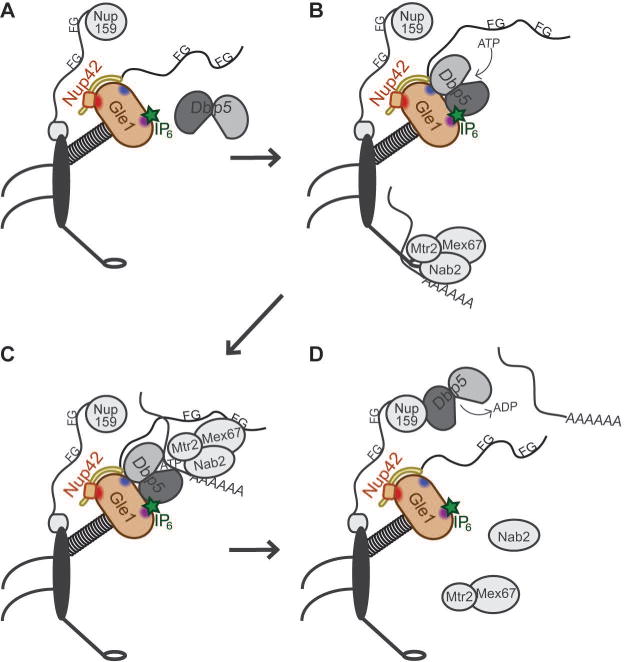
(A) Dbp5 dynamically associates with the NPC. (B) The Nup42 CTD stimulates Gle1-IP6 interaction with Dbp5, with Gle1-IP6 promoting ATP loading onto Dbp5. Mature mRNPs interact with the Mex67-Mtr2 heterodimer via adaptors such as the poly(A)+ binding protein Nab2, permitting export through the NPC. (C) The FG domain of Nup42 recruits the mRNP in close proximity to Dbp5, and Dbp5-ATP binds RNA. Dbp5 might also be a constituent of the exporting mRNP. (D) ATP hydrolysis induces a conformational change in Dbp5 and the bound RNA for release of Nab2, and Mex67-Mtr2, which are recycled into the nucleus for additional rounds of mRNP export. The remodeled mRNP is released into the cytoplasm. Dbp5 interacts with the Nup159 amino terminal domain (NTD) to facilitate ADP release.
