Figure 2.
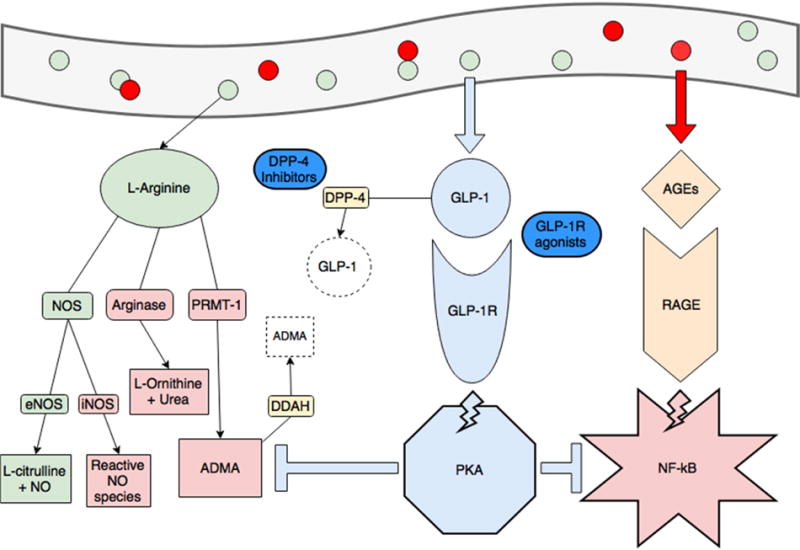
Obesity and consumption of foods high in advanced glycation end-products (red circles, AGEs) creates a pro-inflammatory state through dysregulated arginine metabolism (increasing arginase activity and production of ADMA, in red) and activating RAGE-mediated, NF-kB inflammation (pink star). ADMA also inhibits endothelial NOS (eNOS) and increases NF-kB activity. GLP-1 production is spurred by consumption of L-arginine (green circles) and when binding its receptor, activates protein kinase A (blue octagon). This activity blunts RAGE-mediated inflammation and production of ADMA (blue T-lines). The GLP-1 pathway is also the current target of treatments for diabetes and obesity. GLP-1 is rapidly degraded by DPP-4, and DPP-4 inhibitors (gliptins) are used to increase GLP-1. GLP-1 receptor agonists (exenatide and liraglutide) are also available.
