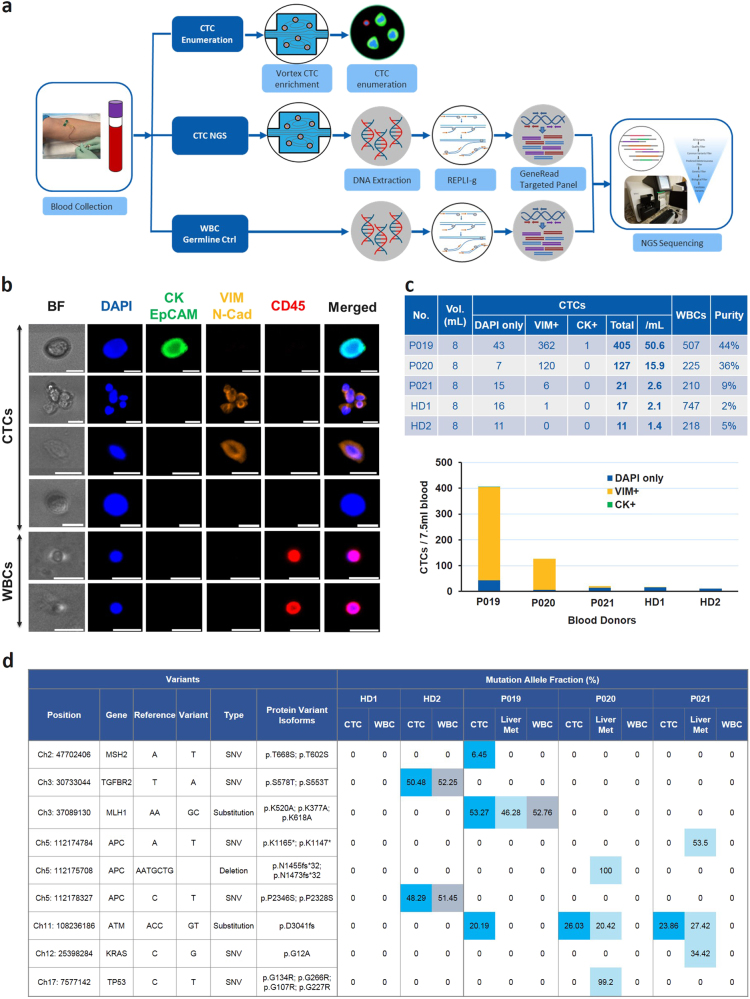
Fig. 7.
Enumeration and mutational profiling of patient CTC samples. a Workflow summary. Blood samples were collected into two EDTA tubes from three CRC patients with resectable hepatic metastases and two age-matched healthy donors. One tube of blood (8 ml) was processed through Vortex technology to collect CTCs for fixation, immunostaining and enumeration. The other tube (8 mL) was also processed through Vortex to collect CTCs for DNA extraction, WGA, PCR, library preparation and MiSeq sequencing. 100 µl of whole blood collected from all patients and healthy donors was stored as the germline control and processed through the same genomic workflow. The sequencing results obtained from the whole blood were compared to the ones of the CTC samples and subtracted as the background. b Picture gallery. Pictures of CTCs and WBCs immunostained with CK, EpCAM, Vimentin, N-Cadherin, CD45, and DAPI. Scale bar represents 20 µm. c CTC enumeration results of each CRC patient and age-matched healthy donor. d Mutation detection in CTCs, liver metastases and WBCs. In all conditions, DNA was extracted and subjected to targeted NGS. The blue/light blue/gray colors highlight the mutations detected in CTCs/liver metastatic tissue/WBCs, respectively, while the number inside each cell indicates the MAF of the mutation. Note that we are calling a genetic variant a SNP when it is also found in corresponding WBCs from the same patient, as in MLH1 in case P019, stressing the importance of including the WBCs as germline controls for each patient