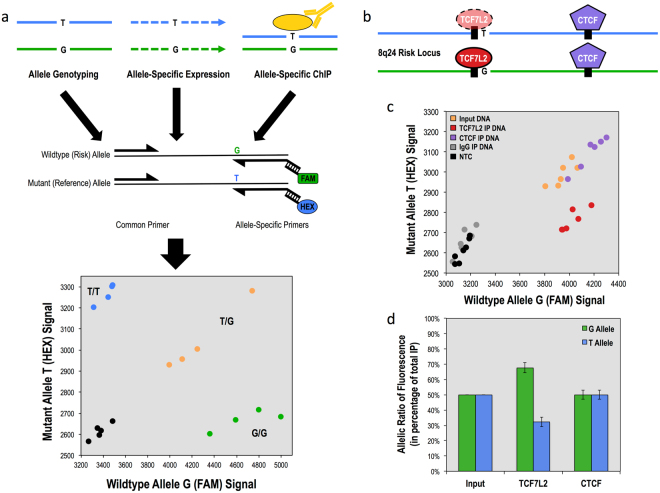
Figure 3.
Allele-specific functional analysis of risk SNP rs6983267 within heterozygous HCT-116 clones using KASP genotyping technology. (a) Overview of the allele-specific applications of KASP genotyping: allele genotyping of nuclease-modified clones, relative allele-specific expression of RNA transcripts harboring a heterozygous mutation and relative allele-specific binding affinity of DNA binding proteins that bind on or in the vicinity of a heterozygous mutation. (b) Diagram of heterozygous 8q24 risk locus with transcription factor TCF7L2 (red) and insulating protein CTCF (purple) with binding motifs depicted as black boxes. Risk SNP is located immediately adjacent to the core TCF7L2 binding motif (TCAAAG). (c) KASP fluorescence ratio output of TCF7L2 and CTCF binding at 8q24 locus between G allele and T allele in heterozygous clones (n = 3) run in duplicate with input genomic DNA (orange), immunoprecipitated DNA for TCF7L2 (red), CTCF (purple) and IgG (gray) and no DNA template controls (black). CTCF IPed DNA samples cluster with Input DNA while TCF7L2 IPed DNA samples create a separate cluster favoring the G allele compared to Input DNA. (d) Allelic ratios of G (green) and T (blue) alleles in percentage of total fluorescence for input control, TCF7L2 and CTCF, quantifying G-allele allelic preference of TCF7L2 compared to CTCF relative to Input DNA control. Errors bars show standard deviation.