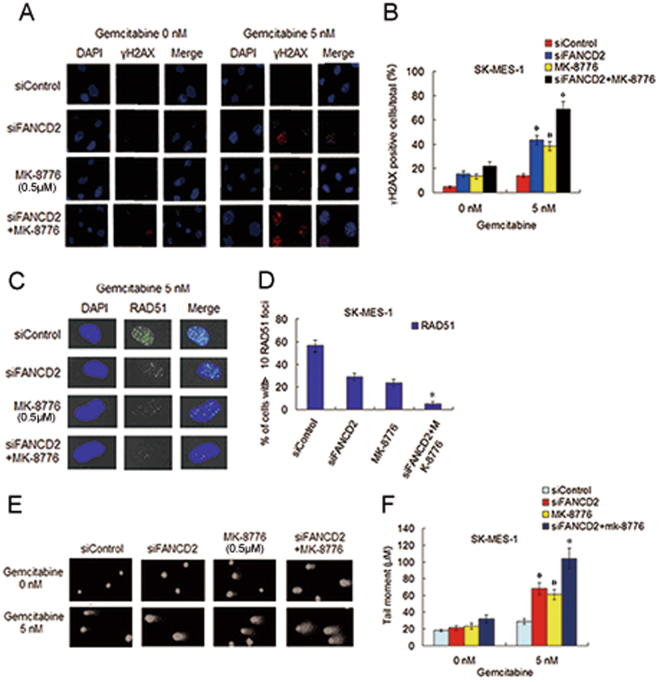
Figure 5.
Depletion of FANCD2 plus MK-8776 treatment in SK-MK-1 cells led to marked accumulation of DNA damage induced by gemcitabine. (A) Before and after transfection with siFANCD2, SK-MES-1 cells were treated with gemcitabine or MK-8776 alone, or gemcitabine plus MK-8776, culture in fresh medium for another 48 h, fixed and immunostained with an anti-γH2AX antibody. (B) The percentage of γH2AX foci positive cells was quantified using Matafer Software (siFANCD2 plus MK-8776 as compared with siControl, *P < 0.001; compared with siFANCD2 or MK-8776, *P < 0.05; siFANCD2 and MK-8776 as compared with siControl, # P < 0.01). (C,D) Before and after transfection with siFANCD2, cells were treated with methods as described above, and fixed and immunostained with RAD51 antibody. The percentage of cells with >10 RAD51 foci was quantified from Image Software (siFANCD2 plus MK-8776 as compared with siControl, *P < 0.001; compared with siFANCD2 or MK-8776, *P < 0.01). (E,F) Before and after transfection with siFANCD2, SK-MES-1 cells were treated with gemcitabine or MK-8776 alone, or gemcitabine plus MK-8776. Alkaline comet assay was used to determine SSBs and DSBs, and the images show detectable comet tail when visualized under a fluorescent microscope. Tail moment in the cells were quantified using Comet Score Software version 1.5 (siFANCD2 plus MK-8776 as compared with siControl, *P < 0.001; compared with siFANCD2 or MK-8776, *P < 0.05; siFANCD2 and MK-8776 as compared with siControl, # P < 0.01).