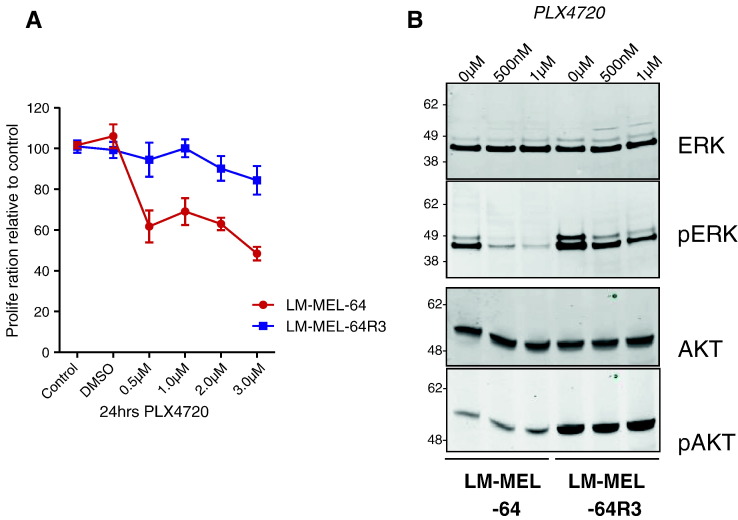
Figure 1.
Generation of a patient-derived melanoma cell line with acquired resistance to the BRAF kinase inhibitor PLX4720. (A) LM-MEL-64R3 is less sensitive to BRAF inhibition. Proliferation as measured by MTS assay of LM-MEL-64 and LM-MEL-64R3 cells in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of the BRAFi PLX4720 (0, 500 nM, 1 μM, 2 μM, and 3 μM) for 24 hours. Data show the mean of three experiments performed in triplicate. (B) LM-MEL-64R3 displays differential MAPK reactivation. Western blot analysis for total and phosphorylated ERK and AKT in LM-MEL-64 and LM-MEL-64R3 in the absence or presence of 500 nM and 1 μM PLX4720 for 4 hours. The cell lines were treated with increasing PLX4720 concentrations (0, 500 nM, and 1 μM), and the effects on MAPK and PI3K signaling were determined by immunoblotting for total ERK and p-ERK1/2, and total AKT and p-AKT levels. Data show representative immunoblots of four independent experiments.