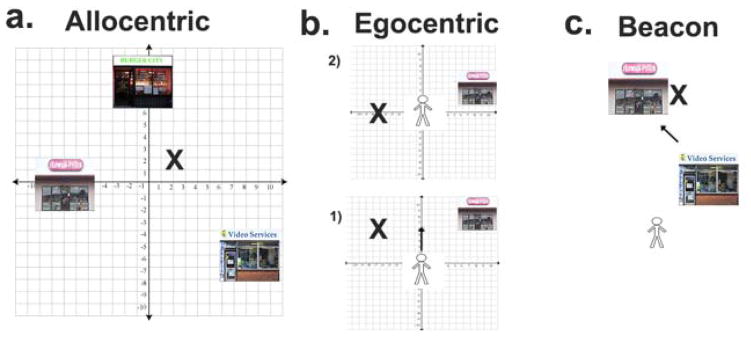
Figure 1.
a. Allocentric navigation: The navigator treats the location of the target (“x”) as a coordinate on a 2-D plane defined by three landmarks (stores). The coordinates in allocentric space are constant as long as the landmarks remain stable. b. Egocentric navigation: The coordinates of the target location (“x”) change continuously with the displacement of navigator from location 1) to 2). In other words, egocentric coordinates change continuously as a function of displacement. c. Beacon/response navigation: The navigator uses the visible locations of stores to find the target. Finding the target is simply based on using its size on the retina to gage the relative distance of the target. Thus, it is not necessary to encode or retrieve a spatial representation or coordinate system when using beacon navigation.