Fig. 4. SCRaMbLE induction of synthetic chromosomes results in multiple types of genome rearrangements.
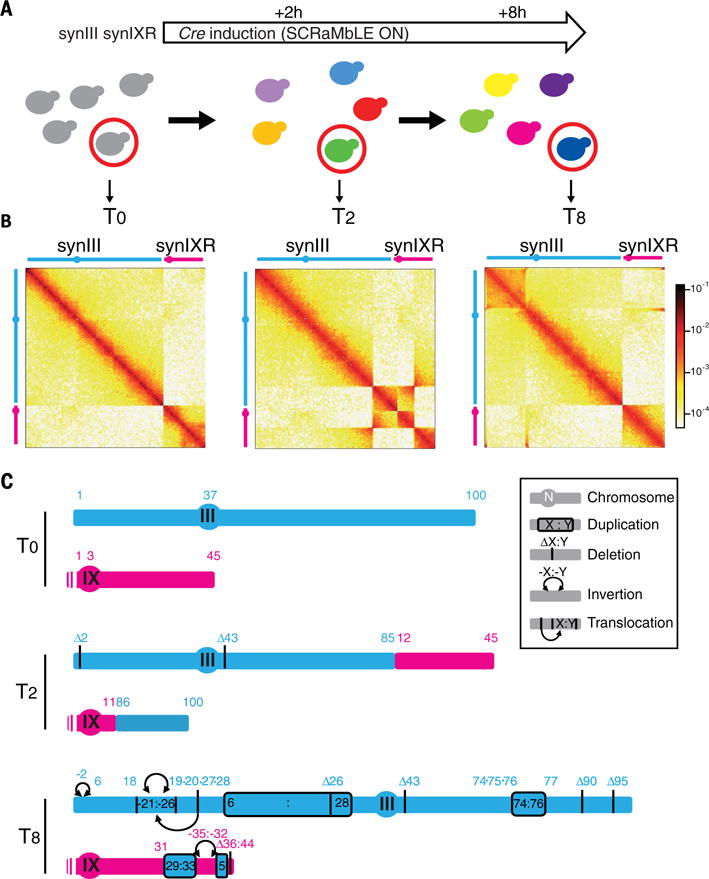
(A) Illustration of the time course induction of the SCRaMbLE system in strain yLM539 carrying two synthetic chromosomes, synIII and synIXR. (B) Normalized contact maps (bin size, 2 kb) of the parental strain yLM539 (at T0; carrying synIII and synIXR) and two SCRaMbLE clones isolated after 2 hours (T2; HMSY029) and 8 hours (T8; HMSY030) of Cre induction. All Hi-C reads are mapped against the reference genome of the parental strain yLM539. (C) Schematic representations of the duplications, deletions, inversions, and translocations identified from these maps and the coverage analysis. DNA segments between two loxPsym sites are numbered from left to right (in blue for synIII and pink for synIX). The schematic representation shows the rearranged synIII and synIX by using numbering of the segments from the parental strain. Details are shown in fig. S18.
