Figure 5.
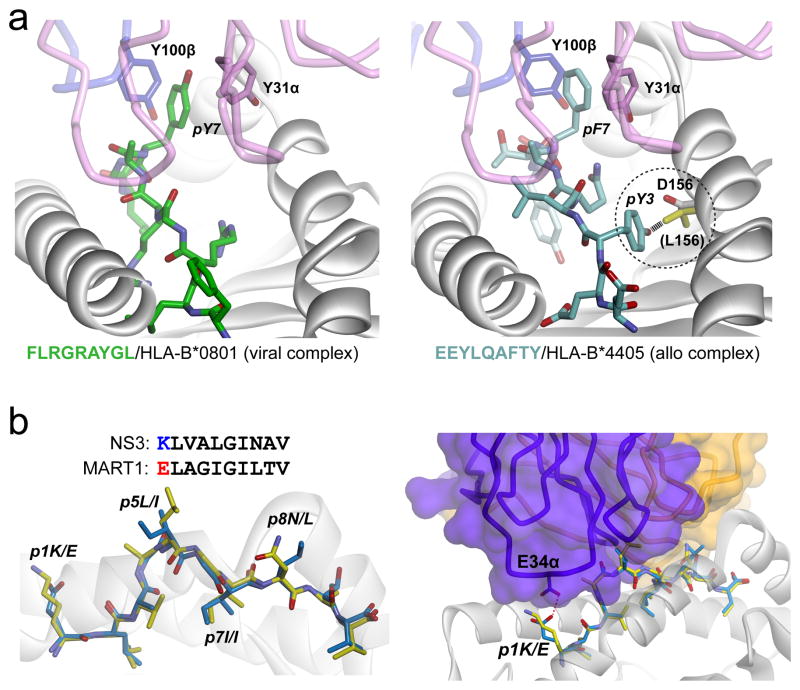
Structural studies of alloreactivity illustrate core principles. A) The LC13 TCR cross-reacts between the syngeneic viral-peptide/HLA-B*0801 complex (left panel) and the allogeneic self-peptide/HLA-B*4405 complex (right panel). Despite considerable sequence differences, the peptides adopt very similar conformations in the ternary complexes, with key interactions between the TCR and the protruding aromatic P7 side chain maintained (86). The TCR also discriminates between closely-related B44 subtypes due to a single amino acid difference that prohibits the peptide from adopting a compatible conformation in B*4403 (right panel, circled detail). In B*4405, the aspartic acid at position 156 forms a hydrogen bond with pTyr3. In B*4403, position 156 is a leucine (yellow) and would clash with pTyr3 as shown. B) In the structure of the HCV1406-NS3/HLA-A2 complex, the conformation and chemistry of the NS3 peptide are similar to those of the MART-126-36 peptide, except for the residue at P1 (left panel). Structurally, the MART-126-35 peptide fits within the complex without any steric clashes or chemical incompatibility, save for the P1 residue, which would experience charge repulsion with Glu134 of CDR1α (right panel). Replacing pGlu1 with lysine resulted in a MART-126-35 variant that was recognized by the HCV1406 TCR (35).