Fig. 4.
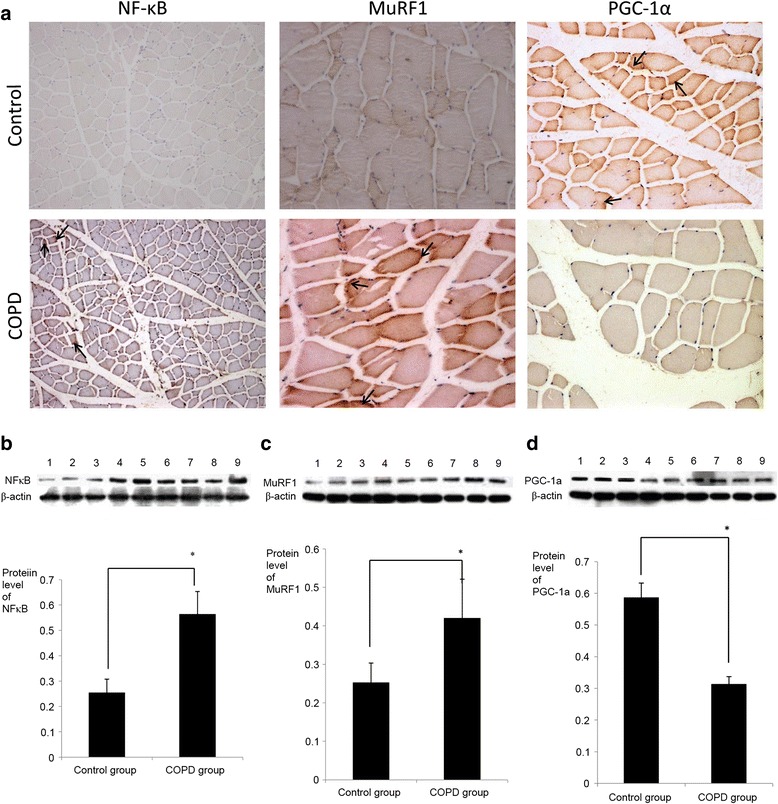
Expression of NF-κB, MuRF1 and PGC-1α in the quadriceps of COPD rats. a Immunohistochemical staining of NF-κB, MuRF1 and PGC-1α in quadriceps samples from control and COPD model rats (NF-κB magnification, ×100, MuRF1 and PGC-1α magnification, ×200). Samples from COPD rats exhibited higher levels of NF-κB and MurF1 and lower levels of PGC-1α, relative to controls. All three factors were localized to the membranes of skeletal muscle cells (black arrows). Subsequent western blot analysis indicated that the changes in b NF-κB, c MuRF1 and d PGC-1α protein expression were significant. Lanes 1–3 represent the control group and lanes 4–9 represent the COPD group. n = 6, *P < 0.05,versus the control group. COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; MuRF1, muscle ring finger-1; PGC-lα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-lα
