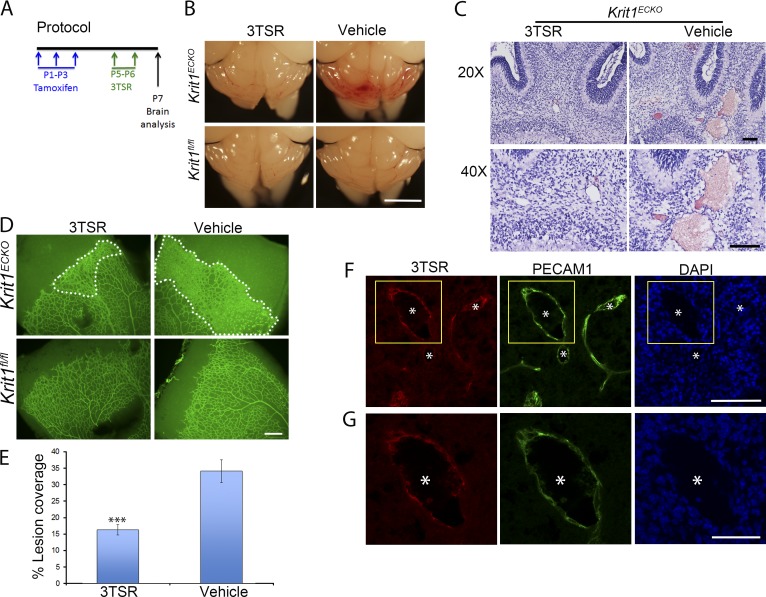
Figure 5.
TSP1 derivative, 3TSR, prevents CCMs and retinal vascular lesions in Krit1ECKO mice. (A) Experimental protocol: vehicle or 3TSR (1.6 mg/Kg) was administered by retroorbital plexus injection at P5 and P6, and brains and retinas were analyzed at P7. (B) Prominent lesions are present in the cerebellum of Krit1ECKO mice, whereas administration of 3TSR suppressed lesion formation. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of cerebellar sections from Krit1ECKO mice after treatment with 3TSR or vehicle (n = 4 mice in each group). (D) Representative image of whole-mount P7 retinal vasculature at the angiogenic growth front. The marked area in Krit1ECKO whole-mount retina shows decreased areas of condensed vascular plexus in Krit1ECKO treated with 3TSR compared with vehicle-treated Krit1ECKO littermates (SEM, n = 8 mice in each group). (E) Quantification of lesion coverage in Krit1ECKO mice treated with 3TSR or Vehicle (SEM, n = 8 mice in each group). (F) Administered 3TSR is present in CCM. 3TSR was injected retroorbitally into a Krit1ECKO;Thbs1−/− mouse. After 30 min, the mouse was killed, and its cerebellar cortex was stained for 3TSR (red, using anti-TSP1 antibodies) and endothelial marker PECAM1 (green); DAPI staining (blue) was used to reveal nuclei. 3TSR is observed in CCM. (G) Higher-magnification images of boxed areas in F. (F and G) Asterisks, vascular lumen of CCM. Bars: (B) 1 mm; (C and F) 100 µm; (D) 200 µm; (G) 50 µm. ***, P < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated Krit1ECKO mice; determined by Student’s t test.