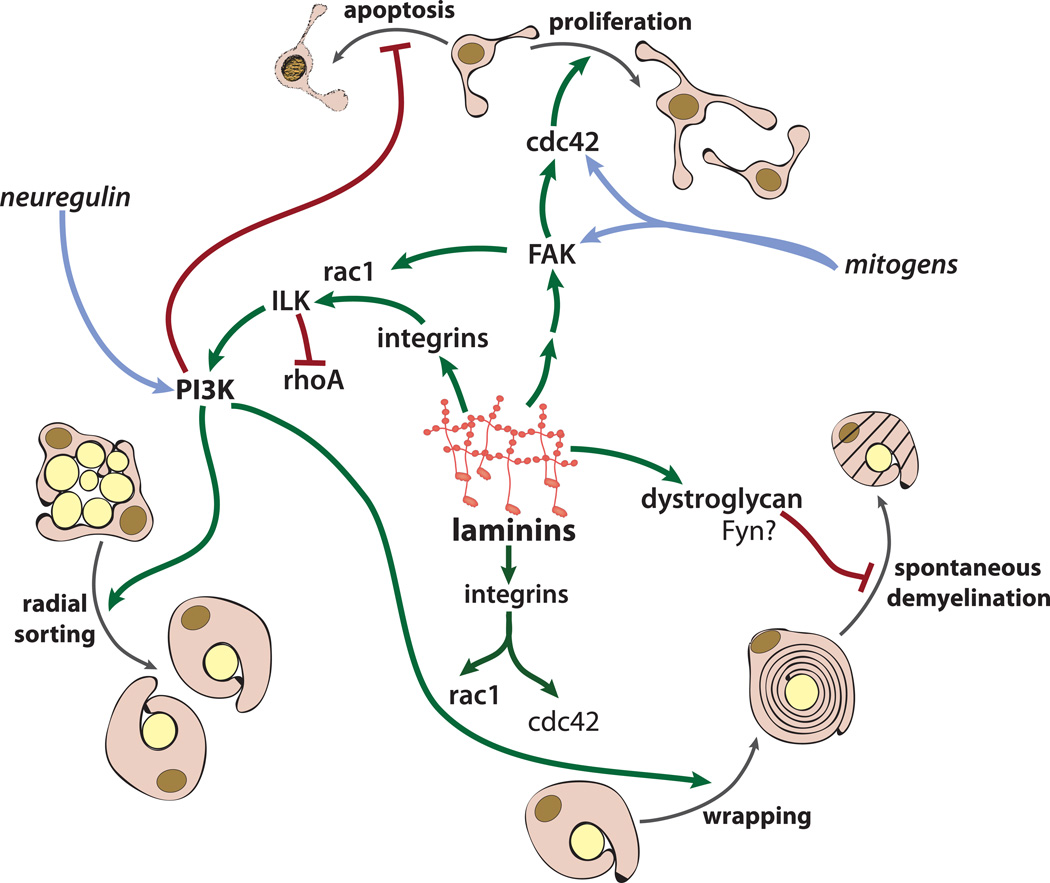
Figure 1. Laminin-modulated signaling pathways regulate multiple stages in Schwann cell development and myelination.
Schwann cell laminins influence multiple cellular events that are necessary for normal Schwann cell development, including survival, proliferation, radial sorting, and myelin wrapping. Laminin β1-subunit containing integrin receptors (here, primarily α6β1) influence the PI3K/Akt pathway by way of ILK to promote Schwann cell survival. Laminins also influence proliferation downstream of FAK and cdc42, although it remains unclear which laminin receptor(s) may be responsible for this effect. Laminin-regulated integrin signaling critically modulates ILK activity, the PI3K pathway, and small Rho family GTPases (activating Rac1 and suppressing RhoA), to control the complex axon-glial interactions that mediate radial sorting. Finally, integrins influence myelin wrapping itself, at least in part by enhancing the activities of the PI3K/Akt pathway, Rac1, and cdc42. Dystroglycan also contributes positively to myelin wrapping but the signaling effectors remain unknown. Dystroglycan, together with α6β4 integrin, is necessary for myelin stability, although the downstream signaling pathways required for myelin maintenance remain unknown.