Table 1.
Attempted chemical oxidationsa
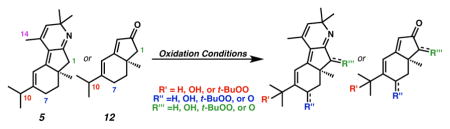
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Conditions | HPLC Yield of Oxygenation Products (%)b,c,d | ||||
| SM | C1 | C7 | C10 | Polyoxygenation | ||
| 5 | SeO2, DCM, 40 °C | 21 | 79 (57)e | – | – | – |
| 12 | SeO2, DCM, 40 °C | 5 | 26 (22) | – | – | 15 |
| 5 | Pd/C (10 wt%), TPHP, 0 °C | 7 | – | 3 | 44 | 46 |
| 12 | Pd/C (10 wt%), TPHP, 0 °Cf | 46 | – | 2 | 42 | 4 |
| 5 | Cr(V) (1 equiv), MnO2 CF3C6H5, 15-crown-5, 80 °C | 55 | 3 | 35g | – | 6 |
| 5 | Rh2(esp)2, T-HYDRO, 23 °C | 2 | 8 | 21(10) | – | 34 |
| 12 | Rh2(esp)2, T-HYDRO, 23 °C | – | – | 15 | 16 | 43 |
See supporting information for reaction conditions and description of the product distribution.
Approximated by separating the products on UHPLC-MS and comparing ion count of the various oxidation products.
Remaining percent balance remaining were unidentified side products.
Numbers given in parentheses indicate isolated yields of the oxidized product.
Protection of 5 to as an N-acyl enamide results in oxidation at C-14.
Shortened reaction time used to observe inherent regioselectivity without over oxidation.
Oxidized product S14 was isolated.
