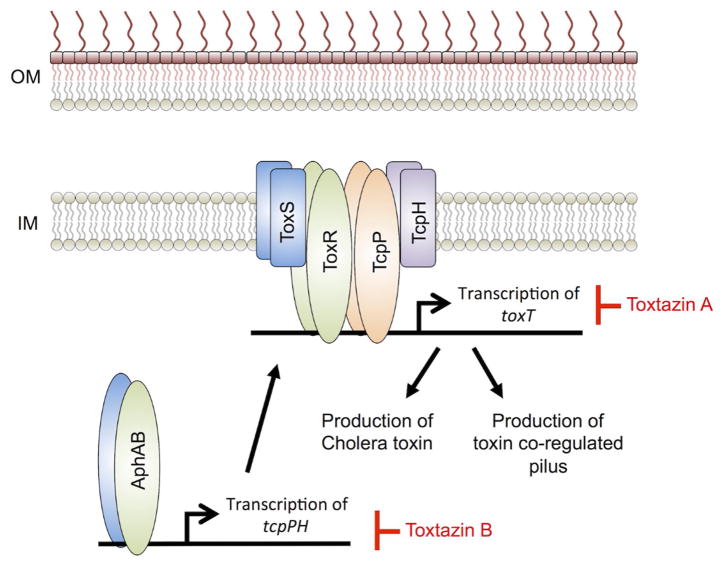
Figure 4. Proposed mechanisms for toxtazins A and B inhibition of cholera toxin and toxin co-regulated pilus production.
ToxT regulates transcription of genes responsible for producing cholera toxin (CT) and the toxin co-regulated pilus (TCP), which are two virulence factors involved in cholera infections. Toxtazin A inhibits toxT transcription and is proposed to act by causing a general stress response, feeding back to shut down transcription of toxT. Toxtazin B inhibits transcription of tcpPH and is proposed to act by reducing intracellular levels of TcpP, leading to reduced transcription of toxT. Inhibitors are in red. OM – bacterial outermembrane; IM – bacterial inner membrane. This model is derived and modified from Anthouard et al. [26]