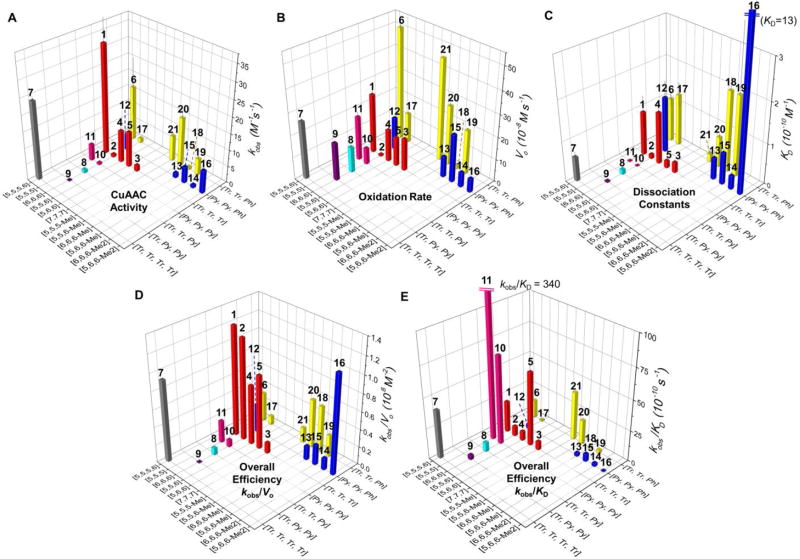
Fig. 3.
Performance of the 21 ligands (1–21) of Cu+. (A) Apparent second-order rate constant (kobs) for the reaction of azido-coumarin AC (100 µM) with propargyl alcohol (50 µM) in the presence of the ligand (100 µM), CuSO4 (100 µM), and sodium ascorbate (5 mM) in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH = 7.4) in air at 24 ± 1 °C during 60 min.57–60 (B) The initial air-oxidation rate (Vo) of sodium ascorbate (200 µM) by diffused O2 in the presence of ligand/Cu(I) 1:1 complexes (100 µM) in PBS (pH = 7.4) at 24 ± 1 °C. (C) Dissociation constants of the Cu(I)-ligand complexes measured by competitive binding assay with Bca. (D) The trade-off between CuAAC over oxidation (kobs/Vo). (E) The trade-off between CuAAC over dissociation constants (kobs/KD). Error bars represent the standard deviation from three-repeated measurement. [m,n,o] represents the chelate arm length. Me in [m,n,o-Me] represents the methyl substitution on the methylene group between central amine and phenyl arm, for 13, 15, 18–21. Me2 in [m,n,o-Me2] represents the methyl substitutions on the 6-position of pyridyl arms, for 14 and 16.