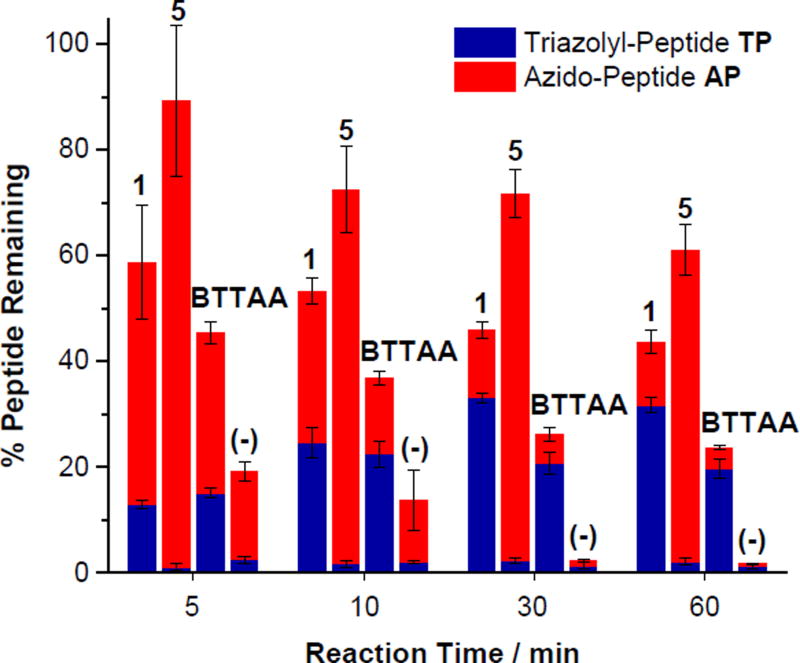
Fig. 6.
Recovery (%) of the azido-peptide peptides AP (red) and the triazolyl-peptide TP (blue) during CuAAC reaction of AP in air with propargyl alcohol. Reaction conditions: the azido-peptide AP (50 µM), propargyl alcohol (50 µM), ligand (100 µM), CuSO4 (50 µM), and sodium ascorbate (500 µM) in Milli-Q water at 24 ± 1 °C. There was no ligand added in the (−) control. The red and blue bars represent the % amount of AP and TP relative to the amount of AP starting material, respectively, measured by LC-MS. The total represents the % peptide starting material and product withstanding the oxidation under the CuAAC conditions. Each data point was the mean of three replicates and the error bar represented the standard deviation.