Figure 3.
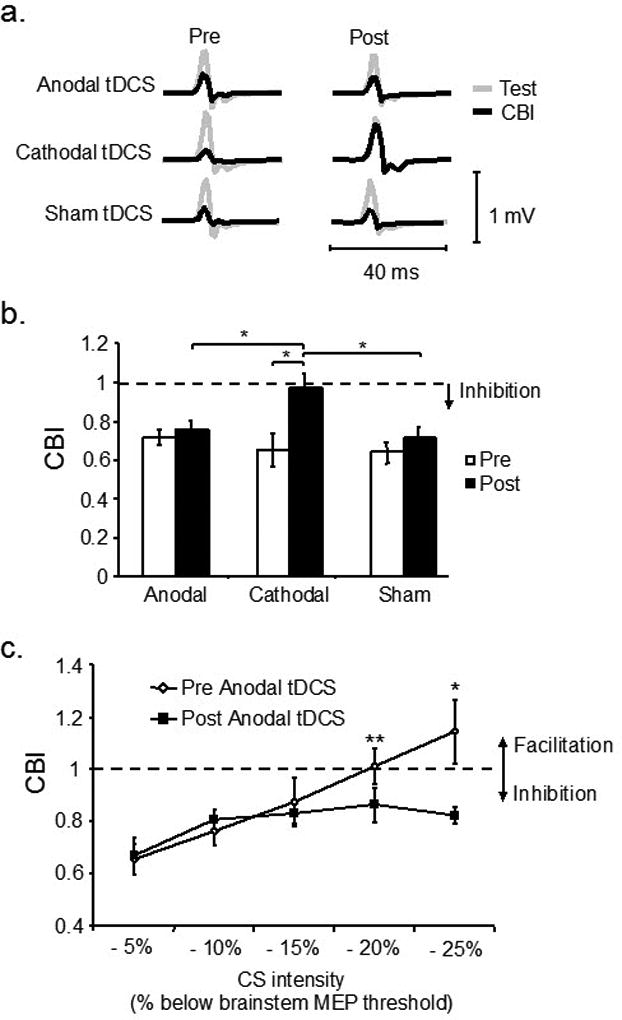
Modulation of cerebellar excitability by tDCS as assessed by CBI. (a) Single EMG traces representing MEP from test (single M1 TMS) and CBI (paired TMS over the CB+M1). Cathodal tDCS reduced CBI. (b) Group data showing magnitude of CBI (ratio of conditioning over test MEP) before and after tDCS. Cathodal tDCS reduces CBI, or the ability of CB TMS to engage the dentate-thalamic-cortical pathway. (c) A recruitment curve of the conditioning TMS intensities over the CB shows that after application of anodal tDCS it is possible to elicit CBI even at very low intensities. In other words, anodal tDCS increased the excitability of the CB. Modified from (Galea et al., 2009) with permission.
