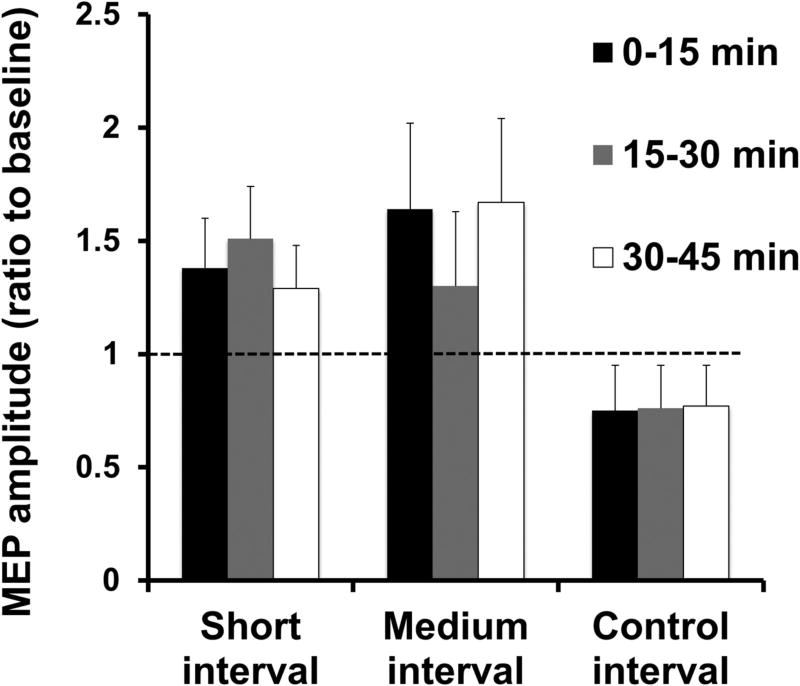
Figure 4.
Induction of plasticity by pairing subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation (STN DBS) and motor cortical transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) at specific intervals in patients with Parkinson’s disease. The short (~ 3 ms) and medium (~23 ms) intervals from STN DBS to motor cortical TMS that produced the greatest cortical facilitation was first determined for each Parkinson’s disease patient. Three plasticity protocols with 180 pairs of STN DBS and motor cortical TMS delivered at the individually determined short and medium intervals and at a control (167 ms, DBS set at 3 Hz) interval were tested. The figure shows the motor-evoked potential (MEP) amplitude from a hand muscle (first dorsal interosseous) at different times after the plasticity intervention as a ratio to the MEP amplitude at baseline before the plasticity intervention. Ratios > 1 indicate facilitation and ratios <1 indicate inhibition. The plasticity protocol increased MEP amplitudes at the short and medium intervals, but not at the control interval. From (Udupa et al., 2016) with permission.