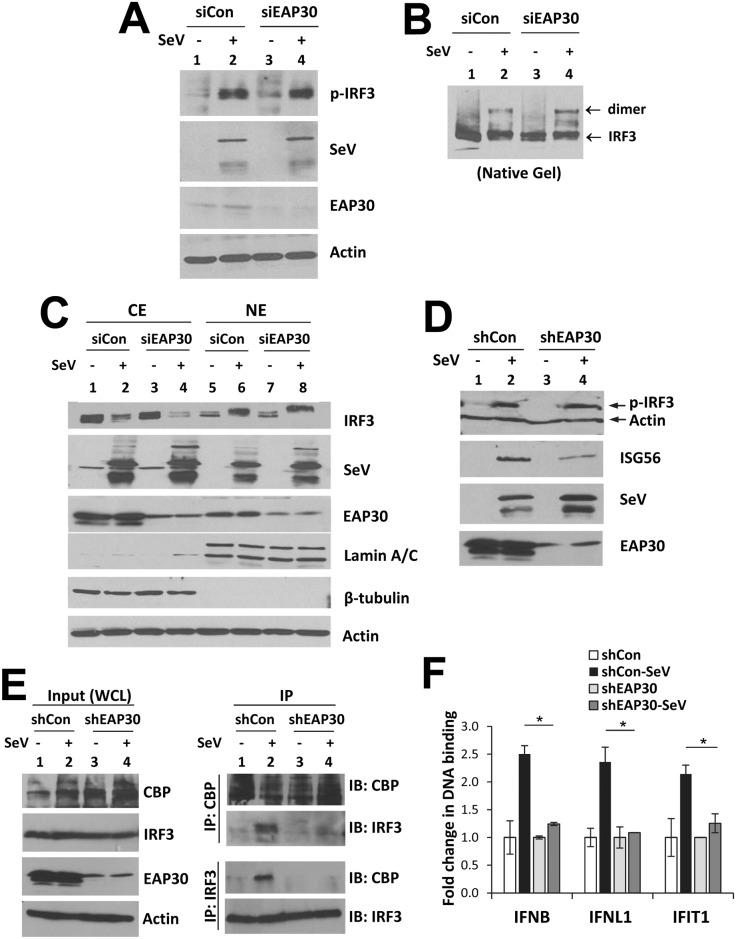
Fig 6. Knockdown of EAP30 does not affect virus-induced IRF3 phosphorylation, dimerization or nuclear translocation, but impairs IRF3-CBP complex formation and IRF3 binding to target gene promoters.
(A) Immunoblotting of phosphorylated-IRF3 (p-IRF3), SeV, EAP30 and action levels in PH5CH8 cells transfected with control or EAP30 siRNA for 48 h and mock-infected or infected with SeV for additional 8 h. (B) Immunoblotting of IRF3 monomer and dimer forms following native PAGE of the samples shown in (A). (C) Immunoblotting of IRF3, SeV, EAP30, lamin A/C (nuclear protein marker), β-tubulin (cytoplasmic protein marker), and actin loading control in cytoplasmic (CE) and nuclear (NE) fractions of PH5CH8 cells transfected with control or EAP30 siRNA and mock-infected or infected with SeV. (D) Immunoblotting of p-IRF3, actin, ISG56, SeV, and EAP30 in HEK293-shEAP30 and HEK293-shCon cells mock-infected or infected with SeV for 8 h. (E) Whole cells lysate (WCL) were collected from HEK293-shEAP30 and HEK293-shCon cells that were mock-infected or infected with SeV for immunoblotting of CBP, IRF3, EAP30 and actin (left panel) and co-IP analysis of virus-induced CBP-IRF3 association (right panel).(F) ChIP analysis of IRF3 binding to IFNβ, IFNL1, and IFIT1 (ISG56) promoters in nuclear extracts of HEK293-shEAP30 and HEK293-shCon cells that were mock-infected or infected with SeV. The ChIP-enriched DNA levels were analyzed by qPCR and normalized to input DNA, followed by subtraction of nonspecific binding determined using control IgG. “*” denotes statistical differences exist with a P-value of < 0.05.