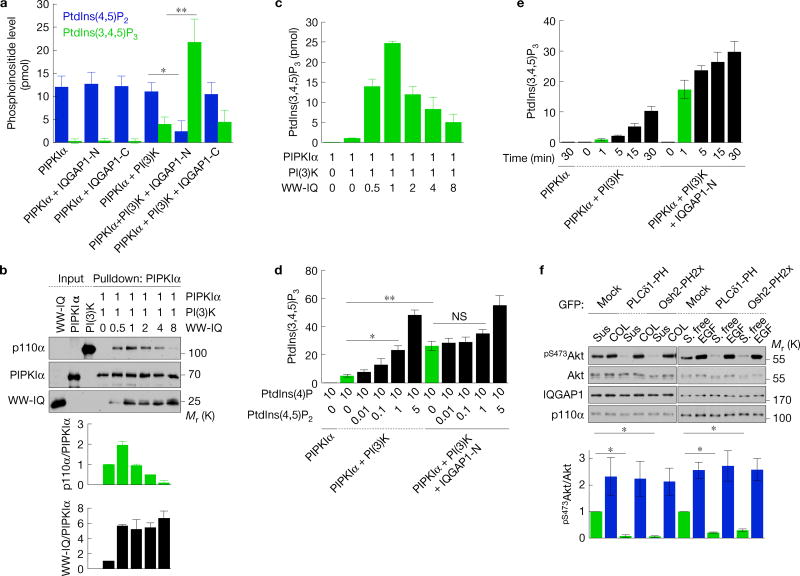
Figure 4.
PtdIns(4,5)P2 produced by PIPKIα is channelled to PI(3)K for PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 synthesis. (a,d,e) PtdIns(4,5)P2 and/or PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 measurement of in vitro kinase assays with PIPKIα, PI(3)K, IQGAP1-N or -C in the indicated combinations. Liposomes containing 10 mol% PtdIns(4)P (for a,e) with the indicated amount of PtdIns(4,5)P2 (for d) were used as substrates, mean ± s.d. of n=4 independent experiments. (b) In vitro binding experiments with PIPKIα, PI(3)K (p110α/p85α) and the WW-IQ fragment (Supplementary Fig. 2a), mean ± s.d. of n=3 independent experiments. The molar ratio of recombinant proteins used is shown. (c) PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 measurement of in vitro kinase assays with PIPKIα, PI(3)K and WW-IQ in the indicated combinations, mean ± s.d. of three experiments. (f) Immunoblotting after replating on type I collagen (COL) for 45 min or 20 ng ml−1 EGF treatment for 15 min in Hs578T cells expressing the indicated PH domains (top), mean ± s.d. of n=3 independent experiments (bottom). P=0.0068, 0.001. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-tests were used for statistical analysis (*,P < 0.05; **,P < 0.01; NS, not significant). Sus, suspension. Source data for a–f can be found in Supplementary Table 1. Unprocessed original scans of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 7.