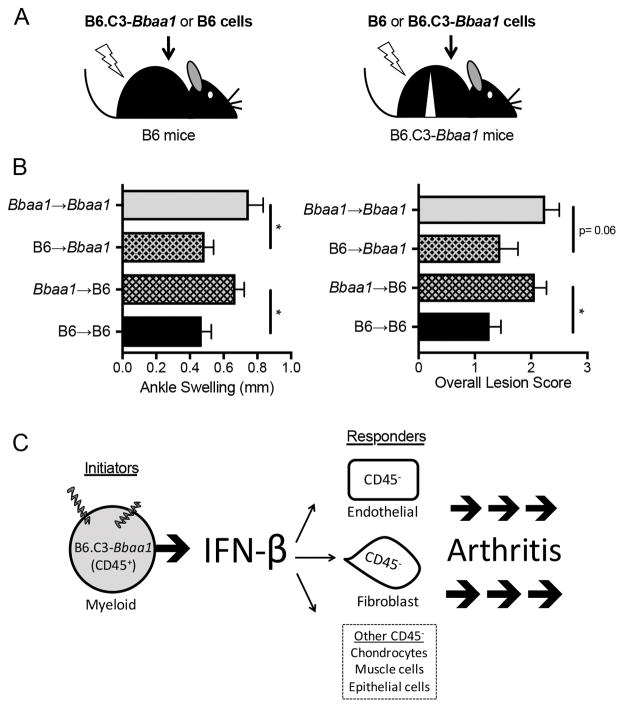
FIGURE 3.
Radiation chimeras between B6 and B6.C3-Bbaa1 mice identify distinct roles for radiation resistant and radiation sensitive lineages in arthritis development. (A) Experimental design: following a lethal dose of irradiation, B6 mice were reconstituted with B6.C3-Bbaa1 splenocytes (Bbaa1→B6) and B6.C3-Bbaa1 mice were reconstituted with B6 splenocytes (B6→Bbaa1). Autologous transplants (B6→B6 and Bbaa1→Bbaa1) were also generated for impact of myeloablative radiation. Arrows indicate direction of transplantation from donor to recipient. (B) Bbaa1 influences arthritis severity through the radiosensitive hematopoietic lineage. Notably, Bbaa1→B6 mice developed the full Lyme arthritis phenotype while B6→Bbaa1 mice were resistant. Arthritis measurements were taken 4 wk post infection with B. burgdorferi (n = 8 to 19 mice per group). Statistical significance was assessed between mice of the same recipient genotype by Student’s t test for ankle swelling and Mann-Whitney U test for overall lesion. *p < 0.05. (C) Model depicting the cellular “pass off” between radiosensitive myeloid (CD45+) cells that initiate IFN-β in response to B. burgdorferi and radioresistant resident (CD45−) cells that respond to IFN-β and drive arthritis development.