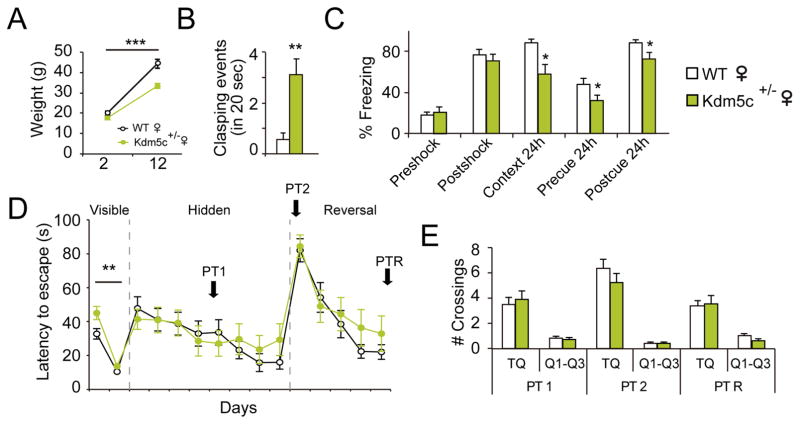
Figure 2. Cognitive impairments are Kdm5c dose-dependent.
A. Kdm5c+/− females are smaller than their WT female littermates (F(1,54) = 17.86, p < 0.0001; post-hoc 12-m p < 0.0001). B. Hemizygous females show hindpaw-clasping (U = 31.50, p = 0.001), although less severe than KO males (see Fig. S2A–B). C. Fear conditioning task: Kdm5c+/− females exhibit fear memory deficits (pre-shock, t27= 0.59, p = 0.6; post-shock, t27= 0.7, p = 0.5; context 24h, U = 57.00, p = 0.04; pre-cue 24h, t27= 2.10, p = 0.05; post-cue 24h, t27= 2.49, p = 0.02). D–E. Morris water maze: The escape latency curve (D) revealed mild learning difficulties during the first day of the task (F(1,54) = 8.91, p = 0.004; post-hoc day 1 p < 0.01), but no difference in performance during the PTs (E). Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. * = p < 0.05; ** = p < 0.005; *** = p < 0.0005 in the Mann-Whitney test, Student’s T-test and two-way ANOVA.