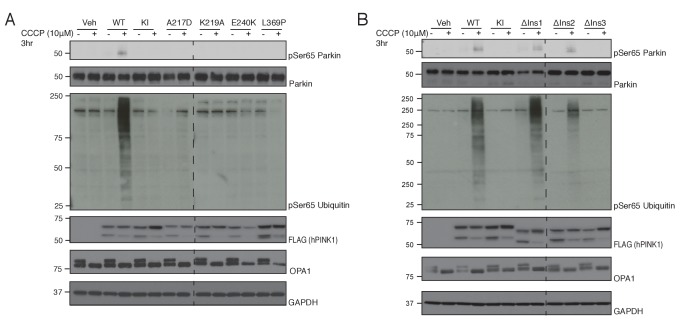
Figure 4. Conservation of ATP and substrate binding mechanism in hPINK1.
(A) hPINK1 knock out HeLa cells transiently co-expressing WT human Parkin and 3xFLAG tagged hPINK1 WT, KI or hPINK1 ATP-binding mutants A217D, K219A, E240K, L369P. A217, K219, E240 and L369 correspond to A194, K196, E217 and L344 of TcPINK1, respectively. Cells were stimulated with 10 μM CCCP or DMSO for 3 hr. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting as follows: pSer65 Parkin (anti-phospho-Parkin); Parkin (anti-Parkin), pSer65 ubiquitin (anti-phospho-ubiquitin), hPINK1 (anti-FLAG), OPA1 (anti-OPA1) and GAPDH (anti-GAPDH). (B) hPINK1 knock out HeLa cells transiently co-expressing WT human Parkin and 3xFLAG tagged hPINK1 WT, KI or hPINK1 Ins mutants ∆Ins1 (180–209 deletion), ∆Ins2 (245–265 deletion), ∆Ins3 (285-294). Cells were stimulated with 10 μM CCCP or DMSO for 3 hr. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting as follows: pSer65 Parkin (anti-phospho-Parkin); Parkin (anti-Parkin), pSer65 ubiquitin (anti-phospho-ubiquitin), hPINK1 (anti-FLAG), OPA1 (anti-OPA1) and GAPDH (anti-GAPDH).