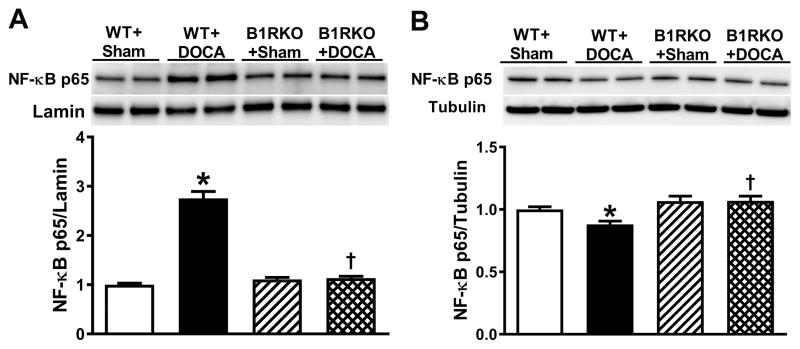
Figure 5. B1R mediated downstream signaling involves NF-κB activation.
NF-κB p65 protein expression was quantified using western blot in brain hypothalamic nuclear and cytosolic fractions from wild-type (WT) and B1R knockout (B1RKO) mice following a 3-week DOCA-salt, or sham treatment. Protein expression was normalized to housekeeping genes Lamin (nuclear proteins) and tubulin (cytosolic proteins). NF-κB p65 levels were significantly increased in nuclear fractions (A) and decreased in cytosolic fractions (B) in hypertensive DOCA-salt-treated mice, indicating activation and translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus. However, no change in NF-κB p65 expression was observed in B1RKO mice with DOCA-salt compared to sham, suggesting that B1R gene deletion prevented NF-κB activation. Data are presented as mean ±SEM. n=6/group. Two-way ANOVA, *P<0.05 vs. WT+Sham, †P<0.05 vs. WT+DOCA.