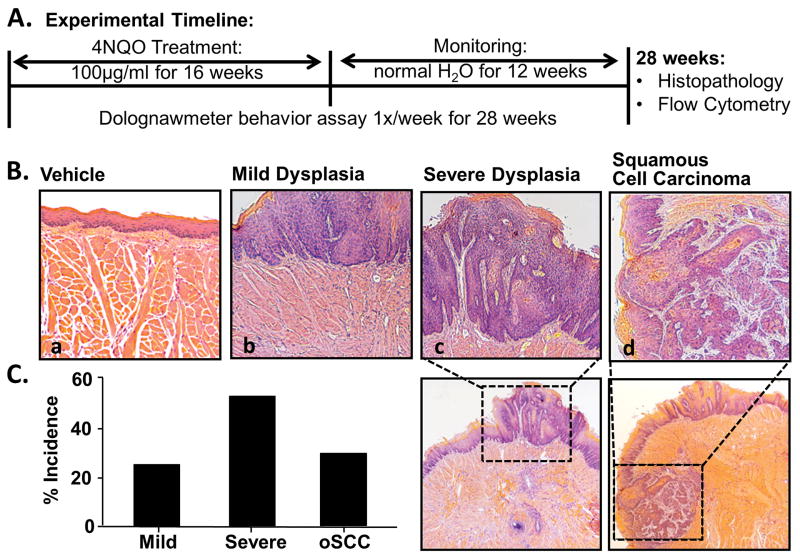
Figure 7. 4NQO-induced mouse model of oral squamous cell carcinoma.
A) Schematic of the experimental design during which a total of 45 mice received either 100 μg/mL 4NQO or propylene glycol (vehicle) in the drinking water ad lib for 16 weeks followed by an additional 12 week monitoring period (normal water). During this time, mice underwent dolognawmeter assay 1× per week for the full 28 weeks to measure functional allodynia during carcinogenesis. At the completion of the study, tongue tissue was processed for histopathology and flow cytometry. B) Representative hematoxylin & eosin stained histological tongue sections from a vehicle-treated mouse (a; 20×) and 4NQO-treated mice with mild dysplasia (b; 20×), severe dysplasia (c; 10× with 20× inset), and invasive carcinoma (d; 10× with 20× inset). 4NQO treatment resulted in lesions within the oral cavity. Pooled data demonstrated the percent incidence of the stages of carcinogenesis.