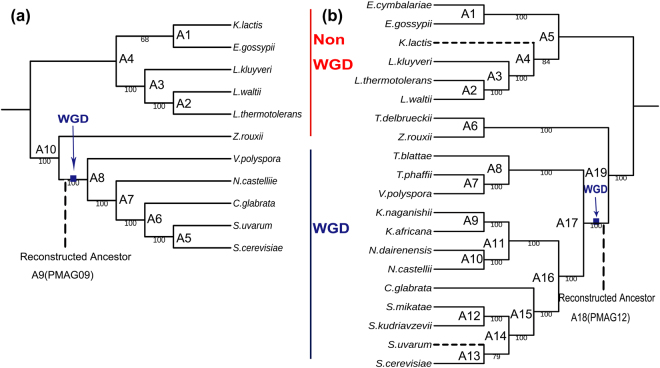
Figure 1.
Yeasts phylogenies built from all types of evolutionary events. The red line shows the non-WGD species, while the blue line shows the post-WGD species. Each leaf represents a species, and each internal node represents a common ancestor. We mark the disagreements between these two phylogenies with dash lines. (a) Phylogeny built for 11 yeast species. All internal edges have bootstrapping values of 100 except the branch between Lachancea genus and Eremothecium genus, which has a bootstrapping value of 68. We label A1–A9 as the reconstructed yeast common ancestors built from the first yeast dataset. The ancestor A9(PMAG09) shows the pre-WGD ancestor PMAG09, which is in the evolutionary step before yeasts’ WGD event. The ancestor A8 is the post-WGD ancestor, had an additional genome copy from the pre-WGD ancestor A9. We also annotate the genes and their functions for all ancestral genomes in Supplementary Table 1. (b) Phylogeny built for 20 yeast species. All of the internal edges have a bootstrapping value of 100 except the branch between Lachancea genus and Eremothecium genus (bootstrapping value of 84) and the branch between the S. cerevisiae and S. uvarum (bootstrapping value of 79). We label A1–A18 as the reconstructed common ancestors built from the second yeast dataset. The ancestor A17(PMAG12) shows the pre-WGD ancestor PMAG12, which is in the evolutionary step before yeasts’ WGD event. The ancestor A17’ is the post-WGD ancestor, had an additional genome copy from the pre-WGD ancestor A17. We also annotate the genes and their functions for all ancestral genomes in Supplementary Table 2.