Fig. 3.
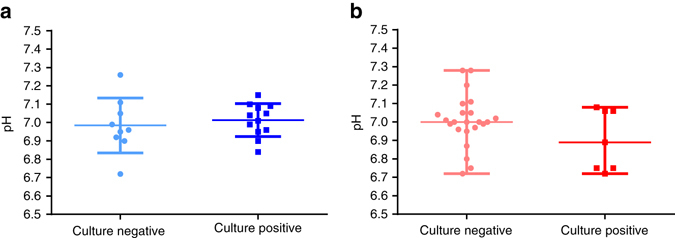
Airway surface liquid pH and infection. a Using a two-sided t-test to determine statistical significance, there was no difference in airway surface liquid pH between patients who had a positive microbiological bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) culture result (n = 12) compared to patients with a negative culture result (n = 9) in the non-CF group (p = 0.59). Mean ± s.d. of airway surface liquid pH was 7.01 ± 0.09 and 6.98 ± 0.15, respectively. Data presented as individual measurements and mean ± s.d. b A two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test demonstrated that there was no difference in airway surface liquid pH between patients who had a positive culture result (n = 7) compared to those with a negative culture result (n = 23) in the CF group. Median (range) of airway surface liquid pH was 6.89 (6.72–7.08) and 7.00 (6.72–7.28), respectively. Data presented as individual measurements and median (range). For all data points, BALF was sampled from the lung lobe corresponding to the airway surface liquid pH measurement. A single pH value was obtained for each individual patient
