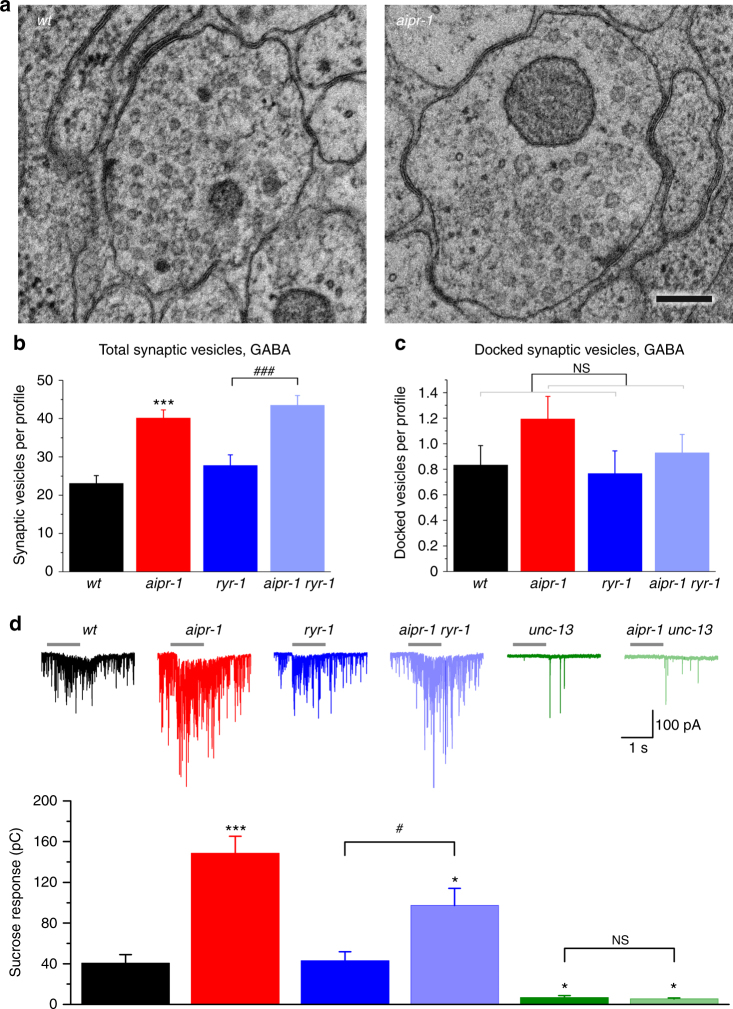
Fig. 8.
Effects of AIPR-1 deficiency on synaptic vesicle number and the size of the readily releasable pool. a Sample micrographs of synapses from wild-type and aipr-1(zw86) animals. b, c airp-1(zw86) increases the numbers of synaptic vesicles b and docked vesicles c. Increases were observed regardless of the ryr-1 genotype. Vesicle numbers compared at GABA synapses among wt (n = 66 synaptic profiles), aipr-1(zw86) (n = 31), ryr-1(e540) (n = 30), and aipr-1(zw86) ryr-1(e540) (n = 56). d aipr-1(zw86) augmented sucrose-evoked postsynaptic currents at the neuromuscular junction regardless of the presence of ryr-1 mutation. The sample size was wt (n = 7), aipr-1(zw86) (n = 8), ryr-1(e540) (n = 7), aipr-1(zw86) ryr-1(e540) (n = 8), unc-13(s69) (n = 7), and aipr-1(zw86) unc-13(s69) (n = 7). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 compared with wt; # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001, ns p > 0.05 compared between indicated groups (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test or Welch’s two-tailed t-test (c) generalized linear model, Poisson family: airpr-1(zw86) effect p = 0.077, ryr-1(e540) effect: NS. Scale bar, 150 nm