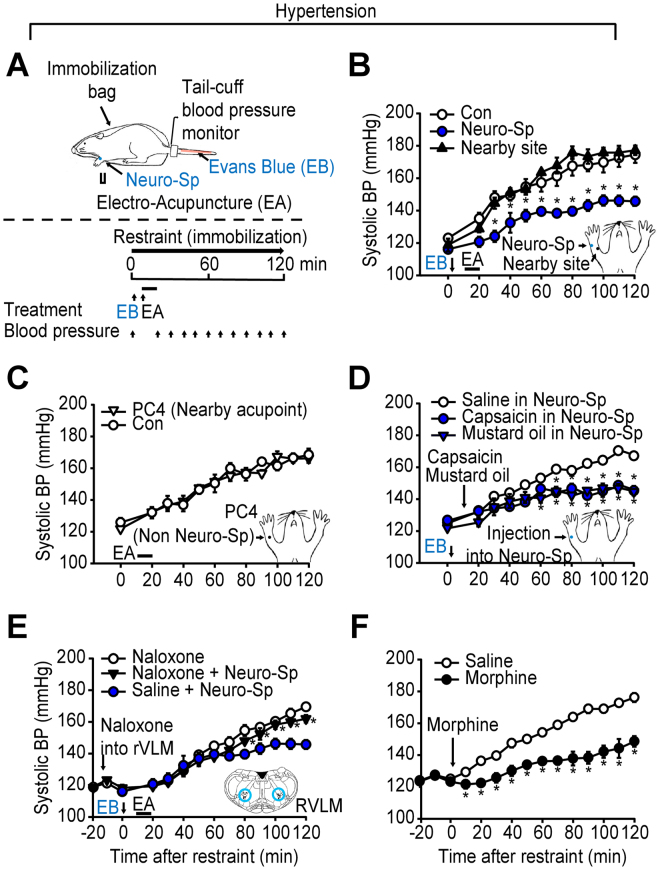
Figure 2.
Stimulation of a neurogenic spot prevents the development of hypertension. (A) Schematic of the experimental procedure in the hypertension model. Evans blue dye (EB) was injected via the tail vein after the initiation of restraint. Approximately 10 min after EB injection, electroacupuncture (EA) at neurogenic spots (Evans blue dots) on the forelimb was applied for 10 min, and blood pressure was measured every 10 min. (B) EA at neurogenic spots prevents the development of hypertension (n = 5–8). *P < 0.05 vs. Con or Nearby site. (C) EA at a non-neurogenic acupoint PC4 fails to suppress hypertension (n = 5). (D) Injection of capsaicin or mustard oil into a neurogenic spot suppresses the development of hypertension (n = 6), while injection of saline in a neurogenic spot does not affect the development of hypertension (Saline in Neuro-Sp). *P < 0.05 vs. Saline in Neuro-Sp. (E) An RVLM injection of naloxone interferes anti-hypertension effects by EA stimulation of neurogenic spot (n = 5), while saline injection into RVLM prior to EA does not affect anti-hypertensive effects of EA (Saline + Neuro-Sp). *P < 0.05 vs. Saline + Neuro-Sp. (F) Intraperitoneal injection of morphine (10 mg/kg) prevents the development of hypertension (n = 7). *P < 0.05 vs. Saline.