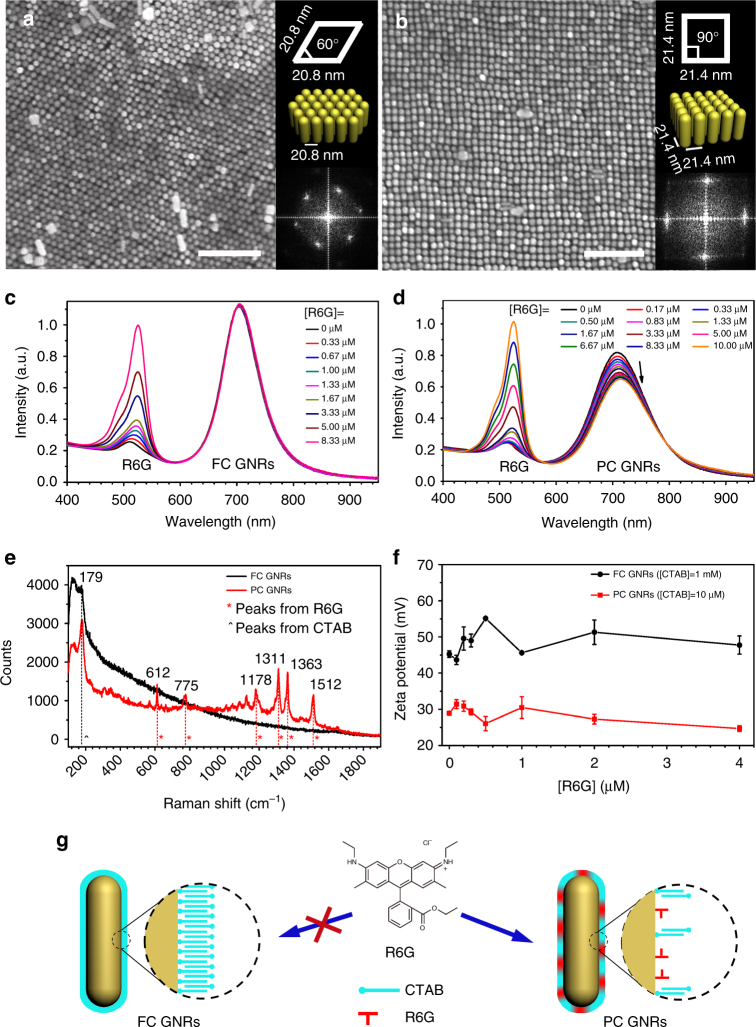
Fig. 1.
R6G-mediated assembly of a tetragonal superlattice of GNRs. a A typical SEM image of hexagonal superlattice (scale bar, 200 nm). Inset (top) presents the corresponding unit cell with parameters (a = b = 20.8 nm, α = 60°). Inset (middle) shows 3D schematics of the hexagonal superlattice. Inset (bottom) is the corresponding Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT) image, confirming hexagonal symmetry of the superlattice. b A typical SEM image of tetragonal superlattice (scale bar, 200 nm). Inset (top) presents the corresponding unit cell with parameters (a = b = 21.4 nm, α = 90°). Inset (middle) shows 3D schematics of the tetragonal superlattice. Inset (bottom) is the corresponding FFT image, confirming tetragonal symmetry of the superlattice. c Effects of R6G on extinction spectra of FC GNRs aqueous suspension. Upon sequential adding of R6G, LSPR band of FC GNRs displays no observable change. d Effects of R6G on extinction spectra of PC GNRs aqueous suspension. With increasing R6G concentration, the LSPR band is gradually red-shifted with a slight decrease in intensity. e SERS spectra of FC and PC GNRs in aqueous solution. Strong characteristic peaks of R6G are observed from PC GNRs, but not from FC GNRs. f Zeta potential of FC and PC GNRs in aqueous solution vs. R6G concentration. Reduced Zeta potential of PC GNRs supports the partial coverage of CTAB bilayer on PC GNRs. For both FC and PC GNRs, increasing R6G concentration, no detected influence of R6G on the Zeta potential of the rods is observed. The mean values and error bars are statistically summarized from three measurements. The error bars represent the standard deviations. g Schematics of R6G and CTAB on rod surfaces. For FC GNRs, fully-covered CTAB hinders R6G to adsorb on the rod surface. For PC GNRs, CTAB partially-covered rod affords enough space for R6G to adsorb