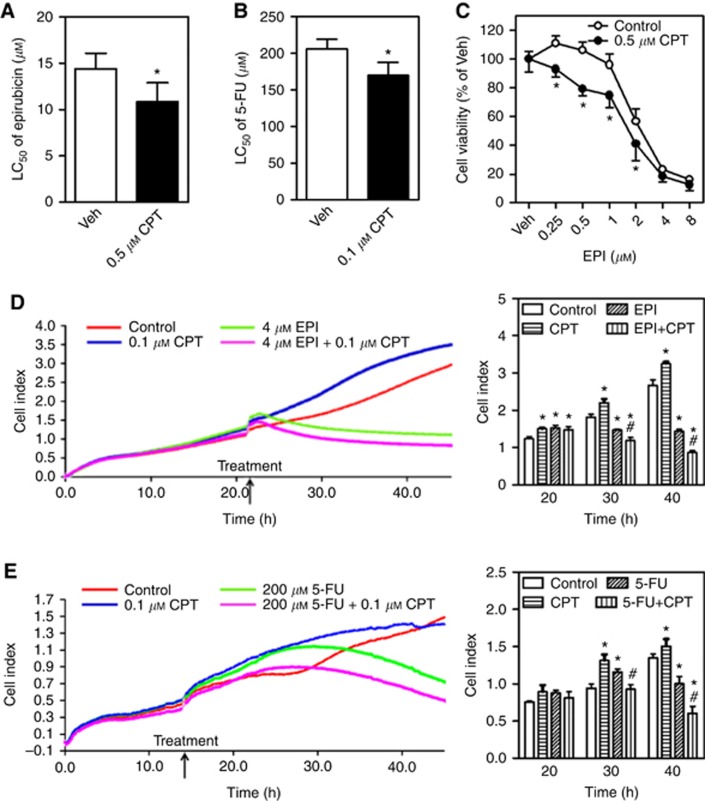
Figure 5.
Camptothecin (CPT) sensitises HCC cells to epirubicin- or 5-FU-induced cytotoxicity. Veh=Vehicle (medium). (A) The HepG2 cells were exposed to various concentrations of epirubicin (EPI) in the presence or absence of 0.5 μM CPT for 24 h and subsequently the cell viability was measured by MTS assay; n=6. *P<0.05 vs Control with the same epirubicin treatment. The LC50 of epirubicin in MTS assay. (B) The HepG2 cells were exposed to 5-FU at different concentrations in the presence or absence of 0.1 μM CPT for 48 h and subsequently the cell viability was measured by MTS assay; n=6. *P<0.05 vs Control with the same 5-FU treatment. The LC50 of 5-FU in MTS assay. (C) The SMMC-7721 cells were exposed to various concentrations of EPI in the presence or absence of 0.5 μM CPT for 24 h and subsequently the cell viability was measured by MTS assay; n=6. *P<0.05 vs Control with the same EPI treatment. (D and E) Cell growth and proliferation were detected by a xCELLigence real-time cell analysis system. The HepG2 cells were treated with 4 μM EPI (D) or 200 μM 5-FU (E) in the presence or absence of 0.1 μM CPT. The proliferation curves (left panels) and cumulative data (right panels) of cells at different times; n=3. *P<0.05 vs Control at the same time. #P<0.05 vs EPI (D) or 5-FU (E) at the same time. A full colour version of this figure is available at the British Journal of Cancer journal online.