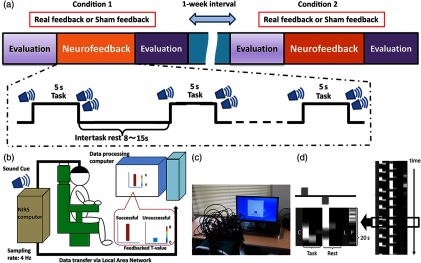
Fig. 2.
Task protocol and NIRS-mediated neurofeedback system. (a) Neurofeedback was applied in the real- and sham-FB conditions on different days with a -week interval. Each session comprised 16 repetitions of a 5-s trial with pseudorandomized rest periods between 8 and 15 s. The order of the task conditions was counterbalanced across participants, who were blind to the task conditions. (b) Participants were asked to raise the FB bar after an auditory cue without any suggestions about how to accomplish this. Successful trials exhibited higher sustained FB values, even in the rest periods, in accordance with the FB -value bar. (c) The NIRS-NFB system in use and user-interface for neurofeedback task. (d) The design matrix for the real-time sliding-window GLM analysis. The time window was 80 data points wide (20 s). The matrix consisted of one constant column () three columns (a hemodynamic response function and its temporal and dispersion derivatives) for the task and rest phases, respectively, one linear term (), and a primary component of the short-distance channel data (). Task-related signal changes were estimated as a -value comparing the task data against the resting data.