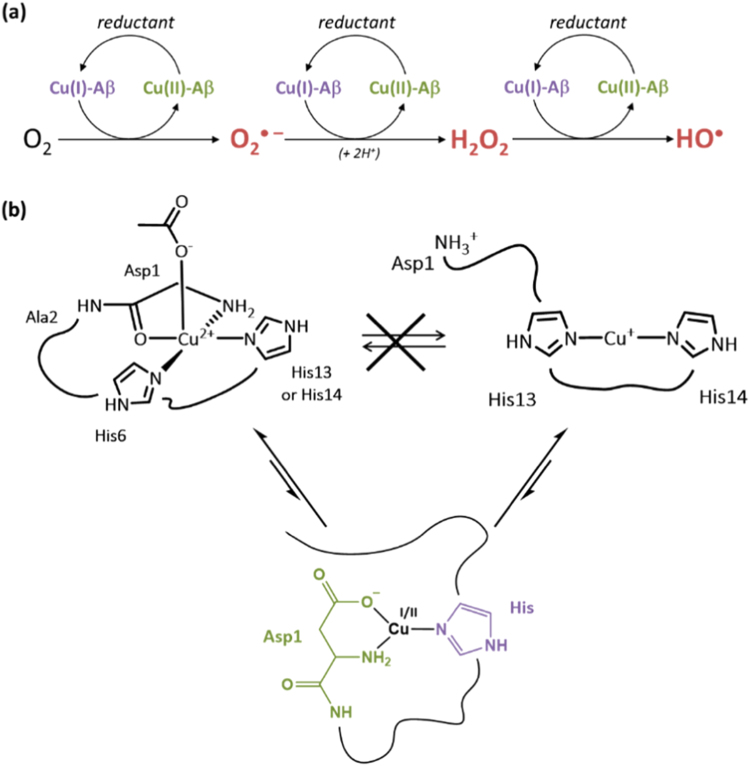
Fig. 5.
(a) Mechanism of ROS production from a reductant and dioxygen catalyzed by the Cu-Aβ complex. The ROS produced are the superoxide anion (O2• −), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and the hydroxyl radical (HO•). (b) Top: Resting states that are the most populated states of Cu(II)-Aβ (left) and Cu(I)-Aβ (right). The redox reaction between these states is sluggish due to a high reorganization energy. Bottom: proposed Cu(I/II) environment in the catalytic in-between state [168].