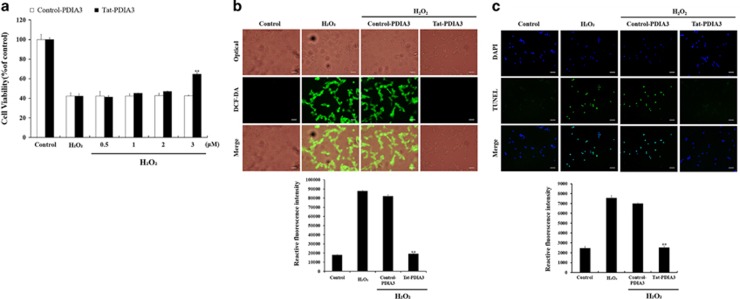
Figure 3.
Protective effects of transduced Tat-protein disulfide-isomerase A3 (Tat-PDIA3) protein against 1 mM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) damage in the NSC-34 motor neuron-like cells. Schematic drawing of experimental design (a). Cell viability, assessed by WST-1 assay, of NSC-34 cells exposed to H2O2, at various doses (0.5–3 μM) of control-PDIA3 or Tat-PDIA3 (b). H2O2-induced ROS production, measured by 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCF-DA) fluorescence intensity, using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plate reader (c). Cell damage based on DNA fragmentation is observed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated biotinylated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining. Scale bar=50 μm (c,d). Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by a Bonferroni’s post hoc test, **P<0.01, which was significantly different from the H2O2-treated group. The bars indicate mean±S.E.M.