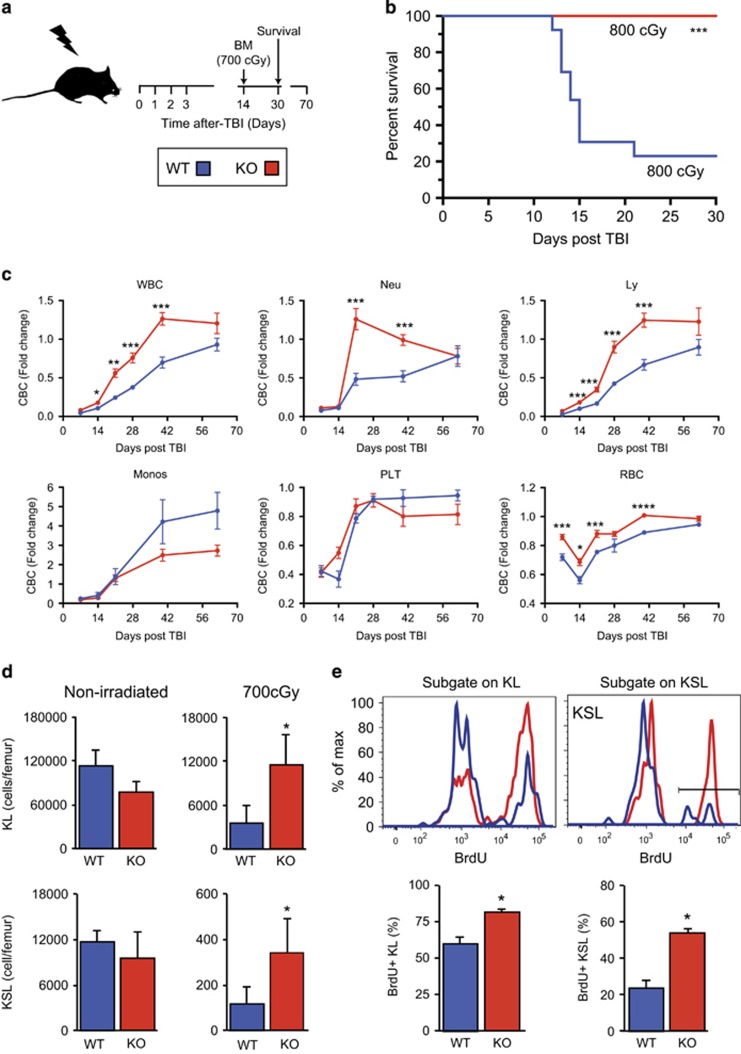
Figure 4.
Camkk2 null mice have improved survival and accelerated hematopoietic recovery following TBI. (a) Scheme of TBI. Mice were TBI and monitored for survival, blood cell count (CBC) and BM recovery. (b) Survival of WT and Camkk2 null mice (WT and KO, respectively) irradiated with 800cGy (n=14 mice per genotype). The blue lines indicate control and the red lines indicate Camkk2 null mice. (c) Hematopoietic recovery in WT and KO mice sublethally irradiated with 700cGy TBI and bled for CBC analysis of total WBCs, platelets (PLT), RBCs, neutrophils (NE), monocytes (Mo) and lymphocytes (Ly) (n=6 and 9 mice for WT and Camkk2 null mice, respectively). (d) WT and KO mice (n=10 per group) were irradiated with 700cGy TBI and euthanized 14 days after irradiation. WT and KO non-irradiated mice were used as controls (n=6 mice per group). Upper and lower bar graphs report mean ±S.E.M. of KL and KSL, respectively. (e) BrdU incorporation in KL and KSL cells in vivo during regeneration. WT and KO mice were irradiated with 700cGy TBI, and after 14 days were pulsed with BrdU in vivo for 2 h before killing. Dot plots of KL and KSL cells and BrdU incorporation on day 14 after radiation (top panels). BrdU staining FACS profiles in KL and KSL subsets (upper panels). Bars graph reports mean±S.E.M. The percentage of BrdU+ cells is shown in lower graphs (bottom panels; n=6 per genotype). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005, ****P<0.001