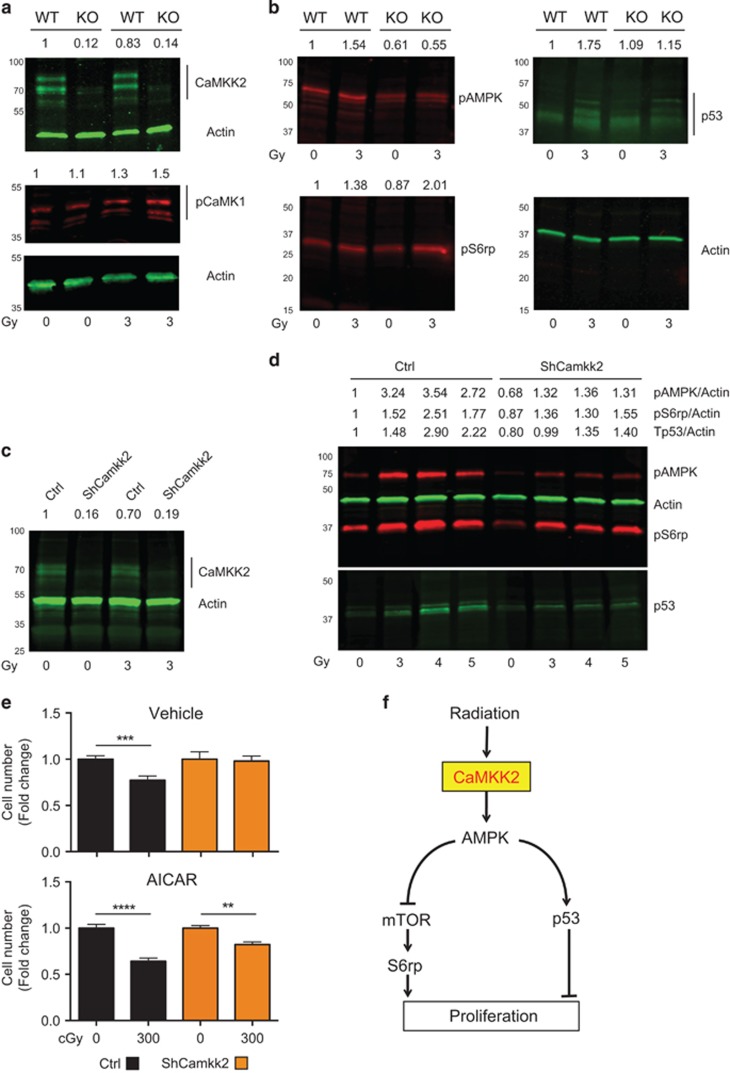
Figure 6.
CaMKK2 couples radiation signaling with the AMPK anti-proliferative pathway. HSPC (KL+KSL) were isolated from WT and Camkk2 null (KO) mice and irradiated in vitro with 400cGy or left non-irradiated. Cells were then cultured for 1-h in regular medium. Protein expression was normalized by actin and expressed as fold change over basal (non-irradiated WT HSPC), and is reported on the top of each lane. (a) Immunoblots of CaMKK2, phospho-CaMK1 (pCaMK1) and actin. (b) Immunoblots of Tp53, phosphorylated AMPK and S6rp (pAMPK and pS6rp, respectively). (c-e) M1 myeloid progenitor cells were transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing a short hairpin sequence for silencing Camkk2 or a control sequence (ShCamkk2 and Ctrl, respectively). Ctrl and ShCamkk2 M1 cells were then irradiated or left non-irradiated. One-hour after irradiation, M1 cell protein expression was assessed by immunoblotting. (c) Expression of CaMKK2 and actin. (d) Immunoblots of pAMPK, pS6rp, actin and Tp53 of M1 cells irradiated with increasing doses of radiation or left non-irradiated. (e) M1 cells transduced with Ctrl and ShCamkk2 lentiviral vectors were 300cGy irradiated and cultured for 24 h in regular medium in the presence or absence of AICAR (100 μM), a cell permeable AMPK agonist (Top and lower, respectively). Cell number was determined using a colorimetric assay, and the results are expressed as fold change of non-irradiated cells cultured in the absence of AICAR. Bars graph reports mean±S.E.M. The experiments included in this figures were replicated at least three times. (f) Modeling the radiation-induced CaMKK2-dependent signal pathway. **P<0.01,***P<0.005, ****P<0.001