Figure 2.
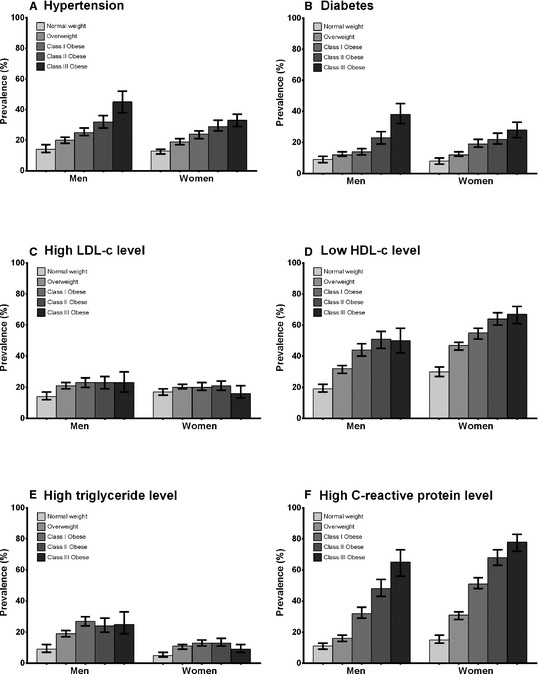
Age‐adjusted prevalence by sex and body mass index category of cardiovascular disease risk factors: hypertension (A), diabetes (B), high low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL‐C) level (C), low high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL‐C) level (D), hypertriglyceridemia (E), and high C‐reactive protein (CRP) level (F). Sex‐specific age‐adjusted prevalence of each CVD risk factor within groups defined by normal weight, BMI ≥18.5 and <25 kg/m2; overweight, BMI ≥25 and <30 kg/m2; class I obesity, BMI ≥30 and <35 kg/m2; and class II to III obesity, BMI ≥35 kg/m2. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure of ≥140 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure of ≥90 mm Hg, or use of antihypertensive medication. Diabetes was defined as fasting plasma glucose of ≥126 mg/dL, 2‐hour postload glucose levels of ≥200 mg/dL, hemoglobin A1c level of ≥6.5%, or use of antidiabetic medication. High LDL‐C level was defined as (calculated) LDL‐C of ≥160 mg/dL or statin use. Low HDL‐C level was defined as <40 mg/dL in men and <50 mg/dL in women. Hypertriglyceridemia was defined as ≥200 mg/dL. High CRP was defined as 3 mg/L to 10 mg/L (individuals with CRP levels >10 mg/L were excluded from analyses). Test for linear trend across BMI categories was P<0.001 for all analyses except for LDL‐C in women, which suggested neither linear (P=0.381) nor quadratic (P=0.644) trends across BMI category. BMI indicates body mass index.
