Figure 3.
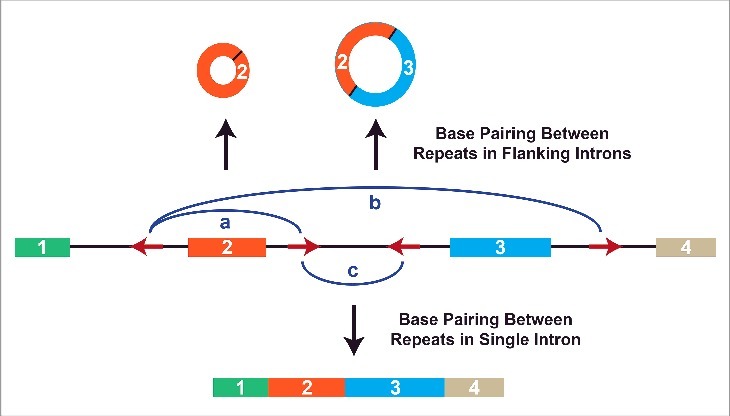
Alternative circularization is driven by competition for base pairing between intronic repeats. Multiple complementary repeat elements (red arrows) are often present in a pre-mRNA. Depending on which repeats base pair to one another (denoted by blue arcs), different pre-mRNA splicing patterns are triggered.40 (a) If the repeats flanking exon 2 base pair to one another, backsplicing is induced to generate a circular RNA comprised of exon 2. (b) A larger circular RNA can be generated if the repeats flanking exons 2 and 3 base pair. This allows backsplicing from the end of exon 3 to the beginning of exon 2. Canonical splicing removes the intron between exons 2 and 3 to yield the mature circular RNA. (c) Alternatively, base pairing between repeats in a single intron leads to canonical splicing and the generation of a linear mRNA.
